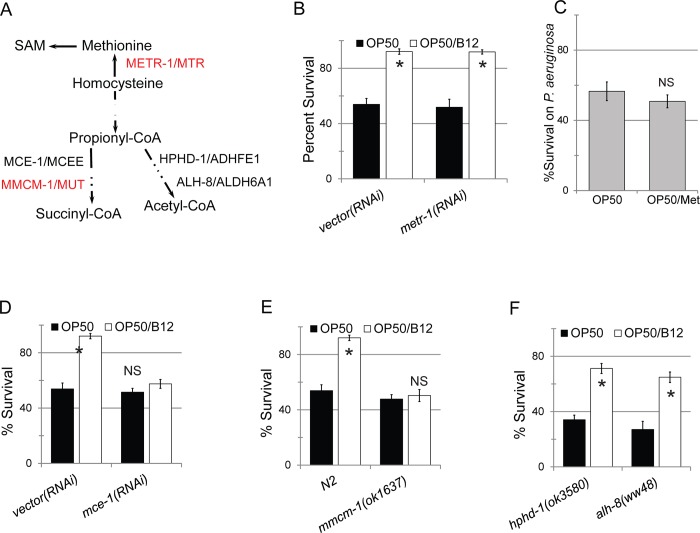
Fig 6. Rescue by methylcobalamin depends on methylmalonyl-CoA/succinyl-CoA clearance.
(A) Schematics of biochemical pathways for methionine and propionyl-CoA metabolism in C. elegans. Proteins in red utilize B12 as a cofactor. (B) Survival of C. elegans fed on E. coli HT115 carrying empty vector or metr-1(RNAi) with or without exogenous methylcobalamin after exposure to P. aeruginosa PA14. (C) Survival of C. elegans reared on E. coli OP50 or OP50 supplemented with L-methionine after P. aeruginosa PA14 exposure. (D-F) Survival of wild-type C. elegans or mutants in two different propionate breakdown pathways with or without methylcobalamin supplementation after P. aeruginosa PA14 exposure. NS–p>0.05, *—p<0.01 based on Student’s t-test. For (B, C, D, E, F) 10 wells, each containing 20 worms, are used per condition per replicate. Three biological replicates were performed for each experiment.