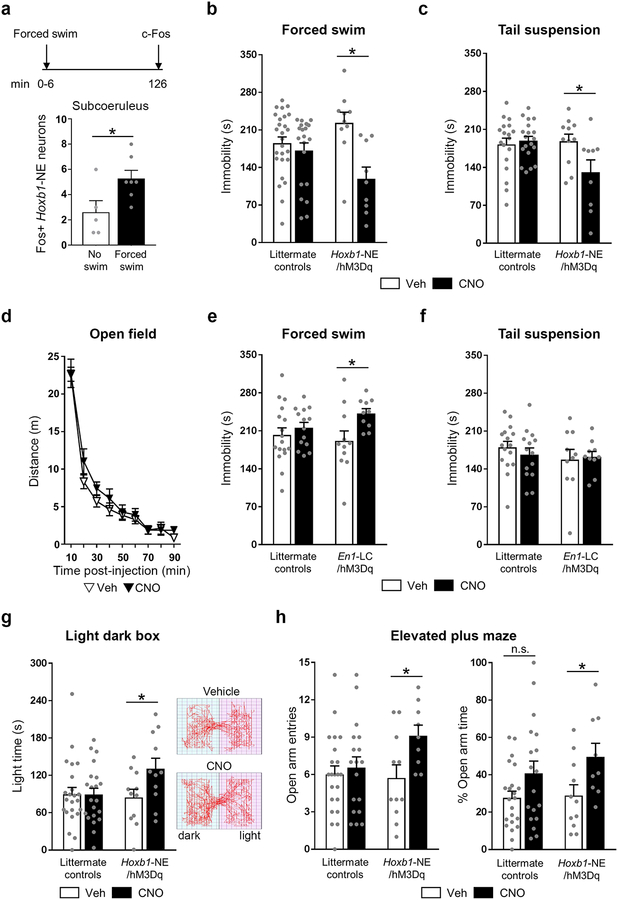
Figure 2. Chemogenetic activation of Hoxb1-NE neurons attenuates behavioral stress responses.
(a) Top: time line of the experiment. Bottom: Fos immunohistochemistry shows that subcoeruleus Hoxb1-NE neurons are activated by forced swim stress (no swim: n=5; forced swim: n=7). (b-c) Activation of Hoxb1-NE neurons reduces immobility time in the forced swim (littermate controls vehicle: n=26; littermate controls CNO: n= 21; Hoxb1-NE/hM3Dq vehicle: n=10; Hoxb1-NE/hM3Dq CNO: n=9) and tail suspension (littermate controls vehicle: n=18; littermate controls CNO: n=19; Hoxb1-NE/hM3Dq vehicle: n=11; Hoxb1-NE/hM3Dq CNO: n=9) tests. (d) Activation of Hoxb1-NE neurons does not affect locomotion in the open field (Hoxb1-NE/hM3Dq vehicle: n=11; Hoxb1-NE/hM3Dq CNO: n=11). (e-f) Activation of LC-NE increases immobility time in the forced swim test (littermate controls vehicle: n=17; littermate controls CNO: n=14; En1-LC/hM3Dq vehicle: n=11; En1-LC/hM3Dq CNO: n=10) but does not affect performance in the tail suspension test (littermate controls vehicle: n=16; littermate controls CNO: n=14; En1-LC/hM3Dq vehicle: n=10; En1-LC/hM3Dq CNO: n=10). (g) Left: Activation of Hoxb1-NE neurons increases time exploring the light compartment of the light dark box (littermate controls vehicle: n=23; littermate controls CNO: n=21; Hoxb1-NE/hM3Dq vehicle: n=11; Hoxb1-NE/hM3Dq CNO: n=11). Right: Representative traces from vehicle- (top) and CNO-treated (bottom) Hoxb1-NE/hM3Dq mice. (h) Activation of Hoxb1-NE neurons increases number of entering (left) and % time exploring (right) the open arm of the elevated plus maze (littermate controls vehicle: n=22; littermate controls CNO: n=18; Hoxb1-NE/hM3Dq vehicle: n=11; Hoxb1-NE/hM3Dq CNO: n=9). Data are mean ± SEM. *P<0.05 vs. no swim (unpaired 2-tailed t-test) or Vehicle (a priori unpaired t-test for light dark box and unpaired 2-tailed t-test following two-way ANOVA for all other tests).