Fig. 1.
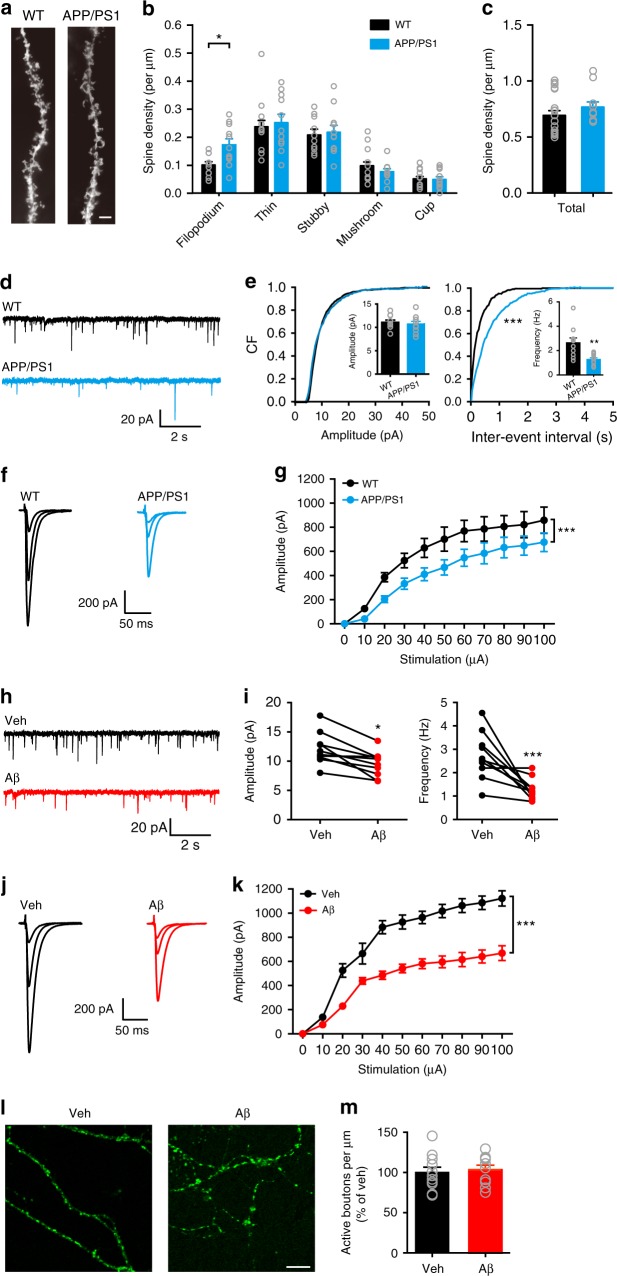
Excitatory synaptic deficits in 6–7-month-old APP/PS1 mice involve a presynaptic mechanism independent of altered bouton density. a–c Representative Golgi staining of apical dendrites (a) and quantification of density of different types of spines (b) and total spine density (c) in CA1 pyramidal neurons in WT and APP/PS1 mice. Bar, 5 μm. t test; *, P < 0.05; N = 10–19 per group. d, e Representative traces (d) of mEPSCs in CA1 pyramidal neurons and cumulative plots and mean values (insets) (e) of mEPSC amplitude (left) and frequency (right) in WT and APP/PS1 mice. Kolmogorov-Smirnov test (cumulative plots), ***P < 0.001; t test (insets), **P < 0.01; N = 10–11 per group. f, g Representative traces of SC-CA1 EPSCs evoked by stimulus intensities of 10, 30, and 100 μA (f) and quantification of EPSC amplitude to stimulus intensity (g) in WT and APP/PS1 mice. Two-way ANOVA with post hoc Bonferroni test; animal, F(1,132) = 30.22, P < 0.001; stimulation, F(10,132) = 27.23, P < 0.001; ***P < 0.001; N = 5–9 per group. h, i Representative traces (h) of mEPSCs in CA1 pyramidal neurons and quantification (i) of mEPSC amplitude (left) and frequency (right) in WT hippocampal slices before (vehicle, Veh) and after Aβ treatment. t test; *P < 0.05; ***P < 0.001; N = 10 per group. j, k Representative traces of SC-CA1 EPSCs evoked by stimulus intensities of 10, 20, 100 μA (j) and quantification of EPSC amplitude to stimulus intensity (g) in WT hippocampal slices before (Veh) and after Aβ treatment. Two-way ANOVA with post hoc Bonferroni test; animal, F(1,132) = 244.0, P < 0.001; stimulation, F(10,132) = 83.89, P < 0.001; ***P < 0.001; N = 7 per group. l, m Representative images of FM1–43-labeled active boutons (l) and quantification of relative FM1–43-labeled bouton density (m) in cultured hippocampal neurons treated with Veh or Aβ. Bar, 50 μm. t test; P > 0.05; N = 10–11 per group. Data are mean ± SEM. CF cumulative frequency. Source data are provided as a Source Data file