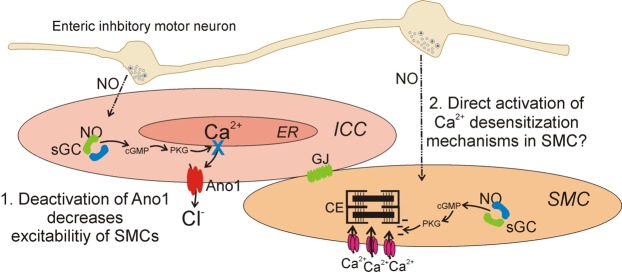
Figure 8.
Tonic inhibition is due to effects on ICC. Schematic illustrating how tonic inhibition affects ICC. Release of nitric oxide (NO) from enteric inhibitory motor neurons activates sGC in ICC, which leads to increased cGMP, and a subsequent decrease in Ca2+ release from ER. Reduced Ca2+ release decreases Ano1 activation, which due to the electrically coupled nature of the SIP syncytium leads to reduced excitability of SMCs. Also possible, but not tested in the current study, might be direct effects of NO on SMCs that may reduce contractions via the NO-sGC-cGMP pathway, leading to desensitization of the contractile element (CE) to cytoplasmic Ca2+.