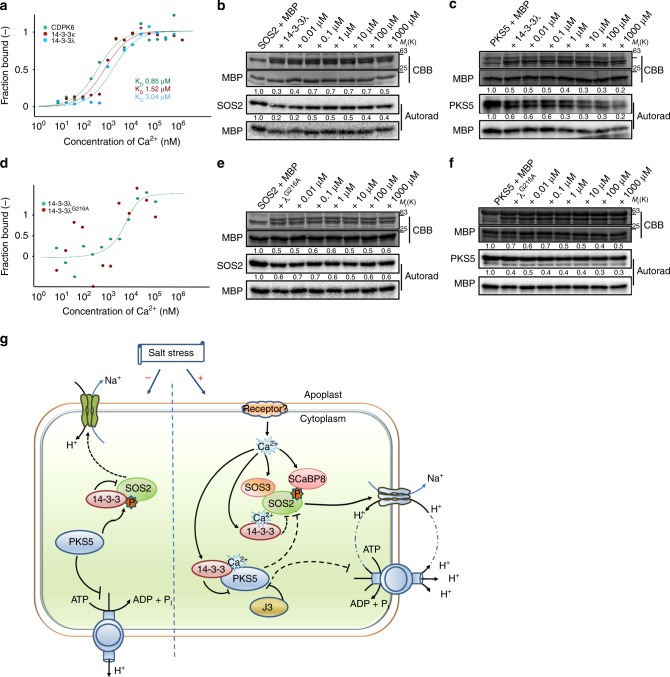
Fig. 7.
14-3-3-mediated regulation of SOS2/PKS5 kinase activity by calcium ions. a MST assay showing that 14-3-3λ and κ interact with calcium ions. CDPK6 served as a positive control. Data are representative of three independent biological experiments. b In vitro kinase assay showing that Ca2+ decreases the 14-3-3-mediated repression of SOS2. c In vitro kinase assay showing that Ca2+ enhances the 14-3-3-mediated repression of PKS5. d MST assay of the Ca2+-binding affinity of 14-3-3λG216A. Data are representative of three independent biological experiments. e In vitro kinase assay showing that the 14-3-3λG216A mutant does not significantly repress SOS2 activity in the presence of Ca2+. f In vitro kinase assay showing that the 14-3-3λG216A mutant does not significantly repress PKS5 activity in the presence of Ca2+. g Model illustrating how 14-3-3 proteins decode a calcium signal to enhance the salt tolerance of plants. Under normal growth conditions, PKS5 phosphorylates SOS2Ser294 and represses SOS2 activity. Upon salt stress, 14-3-3 proteins decode a salt-induced calcium signal, repress PKS5, and release SOS2 to activate PM H+-ATPase and SOS1, respectively. For b and c, about 1.0 µg of 14-3-3λ protein was incubated with or without CaCl2 at a final concentration of 500 µM and 5 mM EGTA at room temperature for 30 min before the kinase assay. MBP was used as a substrate. CBB Coomassie brilliant blue, Autorad autoradiograph. Source data of a–f are provided in the Source Data file