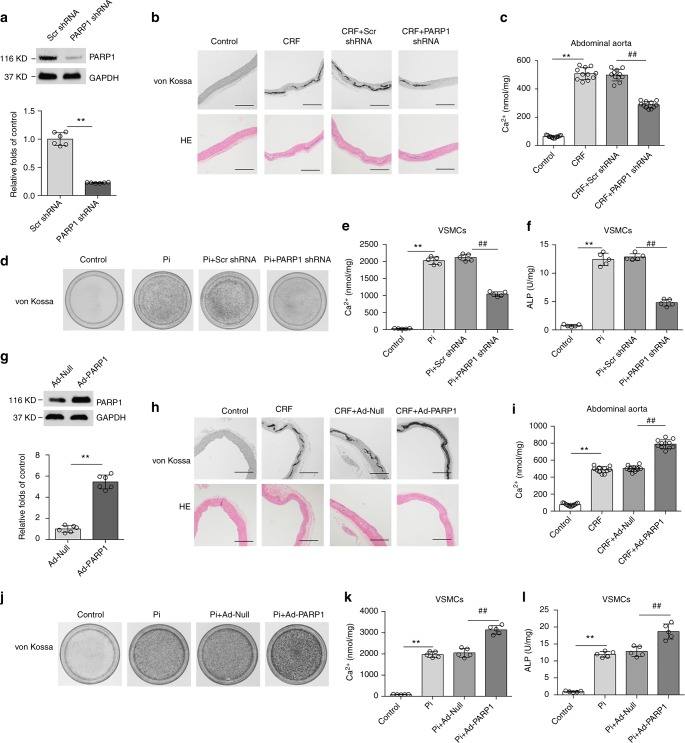
Fig. 2.
Manipulation of PARP1 expression regulates vascular calcification. a–c Rat abdominal aortas were inoculated with adenovirus encoding Scrambled (Scr shRNA) or PARP1 shRNA at three weeks after the adenine diet, and then fed for three weeks. PARP1 deficiency in arteries was identified by western blot (a) (n = 5 per group). Aortas were stained by H&E and von Kossa for mineralization (b), and the calcium deposition in arteries was quantified (c). (n = 10–12 per group). Scale bar, 100 μm. d–f Rat primary VSMCs were pre-infected with Scrambled or PARP1 shRNA adenovirus and then exposed to osteogenic medium for 14 days. VSMCs were stained for mineralization by Alizarin red S (d), and the quantitative analysis of calcium content (e) and ALP (f) were detected respectively. (n = 5 for each group). g–i Rat abdominal aortas were inoculated with Ad-Null or Ad-PARP1 at three weeks after the adenine diet, and then fed for three weeks. PARP1 overexpression in arteries was evaluated via western blot (g) (n = 5 per group). Aortas were stained by von Kossa and H&E for mineral nodules (h) and the quantification of calcium deposition was calculated (i). (n = 10–12 per group). Scale bar, 100 μm. j–l Rat primary VSMCs were pre-infected with Ad-Null or Ad-PARP1 adenovirus and then exposed to osteogenic medium for 14 days. Alizarin red S staining (j), calcium content (k), and ALP (l) in calcified VSMCs were then determined. (n = 5 per group). Statistical significance was assessed using one-way ANOVA for multiple comparison and two-tailed t-tests for two groups and is presented as follows: **P < 0.01 and ##P < 0.01. All values are means ± S.D.