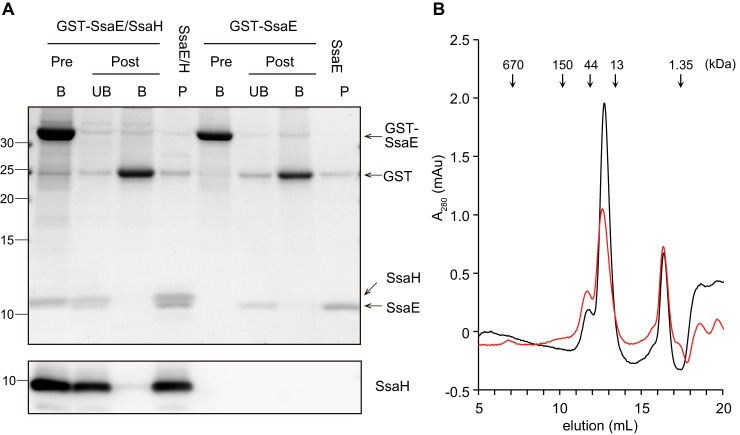
Figure 4.
SsaH directly interacts with SsaE. A, E. coli strains CS7141 (GST-SsaE) and CS7145 (GST-SsaE and SsaH) were grown to exponential phase followed by the induction of GST-SsaE and SsaH by the addition of 1 mm IPTG for 3 h. GST-SsaE in each cell lysate was bound to MagneGST glutathione particles for 1 h at 4 °C. After washing, the particles were divided into two groups. One part was incubated with 50 mm GSH to elute GST-SsaE and bound proteins (Pre, B). The other was incubated with PreScission protease for 16 h at 4 °C to cleave the GST tag from the SsaE protein. Next, cleaved proteins were collected (Post, UB), and the proteins bound to particles were eluted (Post, B). P indicates the peak fraction separated using gel-filtration chromatography. Proteins separated via 16% Tricine gel were visualized with Oriole fluorescent gel stain (upper panel) and immunostained with anti-SsaH antibody (lower panel). B, stoichiometric analysis of SsaE (molecular mass, 9.65 kDa) and SsaE-SsaH (molecular mass, 10.3 kDa for SsaH and 20 kDa for the complex) via gel filtration. A total of 12 μg of each of SsaE–SsaH (red) and SsaE (black) protein was subjected to size-exclusion chromatography using Superose 12. Absorbance at A280 was monitored to determine the elution profile. mAU, milliabsorbance units.