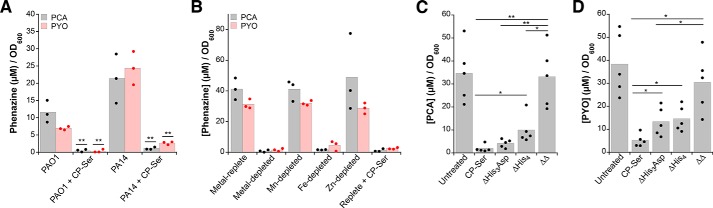
Figure 5.
CP and iron depletion inhibit phenazine production. A, average PYO and PCA concentrations in supernatants from P. aeruginosa PAO1 and PA14 cultures grown in the absence or presence of 10 μm CP-Ser (n = 3; **, p < 0.01). B, average PYO and PCA concentrations in supernatants from PA14 cultures grown in metal-depleted Tris/TSB supplemented with the indicated metals in the absence or presence of 10 μm CP-Ser (n = 3). For comparison with the replete condition, p < 0.01 for PYO and PCA levels in depleted, iron-depleted, and replete + CP-Ser conditions. C and D, effect of CP variants on phenazine production. Average PCA (C) and PYO (D) concentration in supernatants from PA14 cultures grown in the absence or presence of 10 μm CP-Ser, ΔHis3Asp, ΔHis4, or ΔΔ (n = 3; *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01). For comparison with the untreated condition, p < 0.01 for CP-Ser, ΔHis3Asp, and ΔHis4 (C) and p < 0.01 for CP-Ser and p < 0.05 for ΔHis3Asp and ΔHis4 (D). A–D, cultures were grown at 37 °C for 8 h. Supernatants were analyzed by HPLC alongside a standard curve, and integrated phenazine peak areas (absorption at 365 nm) were converted to concentration. Phenazine concentrations were normalized to the A600 of their respective cultures. Culture A600 ranged from 1.6 to 3.1.