Figure 2.
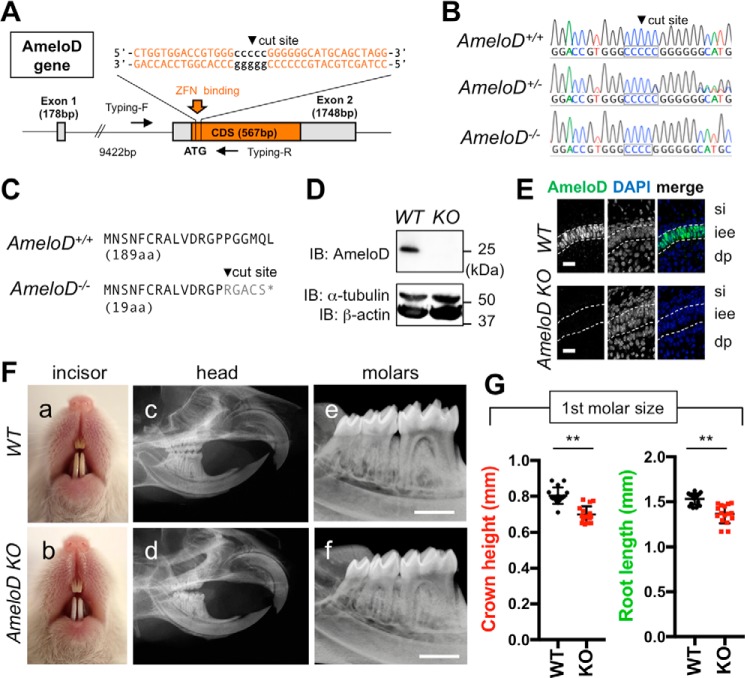
Generation of AmeloD-KO mice. A, targeting strategy for AmeloD-KO mice. ZFN binds near the cut site and deletes 1 bp in the cut site. Arrows indicate primer locations for genotyping. CDS, coding sequence. B, DNA sequences of the ZFN-binding site in the AmeloD locus. The cut site is shown in the boxed region. In AmeloD−/− (KO) mice, 1 bp was deleted from the cut site. In the AmeloD+/− (heterozygous) mice, both WT and KO alleles were detected. C, comparison of the AmeloD amino acid sequence of the WT and AmeloD-KO product. In AmeloD-KO mice, the frameshift caused an early termination codon, resulting in a short protein consisting of 19 aa. D, protein expression of AmeloD in WT and AmeloD-KO P1 molars. The AmeloD protein was stained with the AmeloD antibody (molecular mass, 25 kDa). α-Tubulin (molecular mass, 52 kDa) and β-actin (molecular mass, 42 kDa) are shown as internal controls. IB, immunoblotting. E, immunofluorescence staining analysis of AmeloD in WT and AmeloD-KO P1 molars. Green, AmeloD; blue, DAPI for nuclear staining. si, stratum intermedium; iee, inner enamel epithelium; dp, dental pulp. The dashed lines indicate the borders of IEE cells. Scale bars, 20 μm. F, photographic analyses (a and b) and radiographic analysis (c–f) of 6-week-old WT and AmeloD-KO heads. Skeletal bone abnormality was not observed between WT and AmeloD-KO mice. Scale bars, 1000 μm. G, the crown heights and root lengths of extracted first molars from 6-week-old WT and AmeloD-KO mice (n = 16). The mean is shown as lines. Error bars represent S.D. **, p < 0.01 with a two-tailed t test.