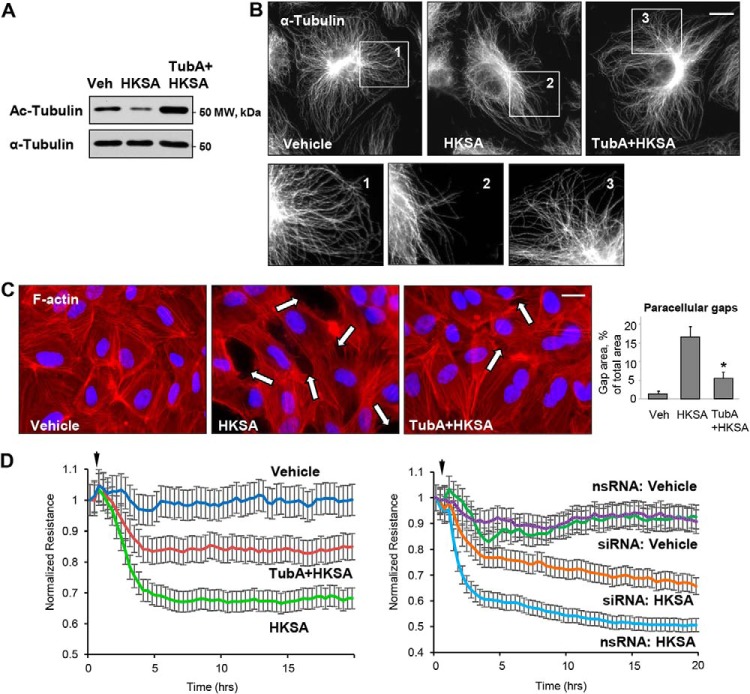
Figure 3.
HDAC6 inhibitor attenuates HKSA-induced EC barrier dysfunction. HPAEC were treated with vehicle (Veh) or HDAC6 inhibitor TubA (10 μm, 30 min) followed by HKSA challenge (2 × 108 particles/ml, 6 h); MT integrity, actin cytoskeleton remodeling, and paracellular gap formation were monitored. A, top, acetylated tubulin levels were determined by Western blotting. Bottom, depicts total α-tubulin levels in samples. B, microtubule organization was monitored by immunofluorescence staining with α-tubulin antibody. The outlined areas in the top row (inserts 1–3) are depicted as corresponding higher-magnification images in the bottom row, revealing details of peripheral MT organization. Bar = 5 μm. C, cells were stained with Texas Red phalloidin to visualize F-actin. Cell nuclei were visualized by DAPI counterstaining. Paracellular gaps are shown by arrows; bar = 10 μm. Shown are representative results of three independent experiments. Veh, vehicle. D, cells were stimulated with HKSA (arrowheads) in the presence or absence of TubA (left panel), or they were transfected with HDAC6-specific or nonspecific siRNA prior to HKSA challenge (right panel). TER was monitored over a 20-h time period.