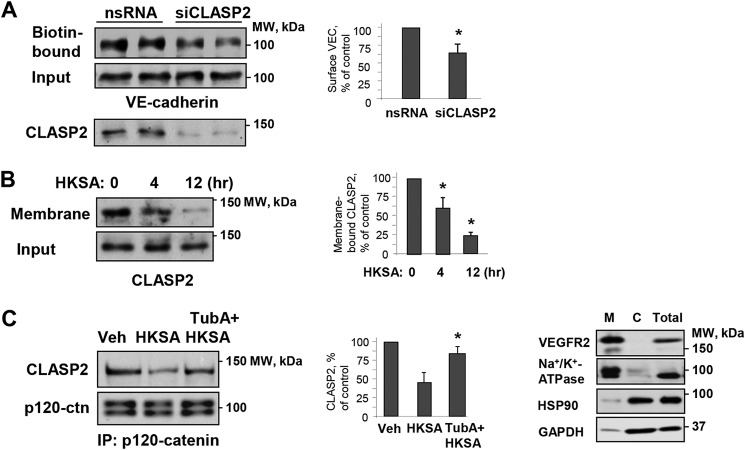
Figure 5.
Role of MT plus-end–binding protein CLASP2 and microtubules in modulation of HKSA-induced cell junction dysfunction. A, HPAEC were transfected with CLASP2-specific (siCLASP2) or nonspecific siRNA (nsRNA) for 72 h, and a surface protein biotinylation assay was performed for VE-cadherin. The efficiency of endogenous CLASP2 knockdown was confirmed by membrane reprobing with CLASP2 antibody. B, cells were treated with HKSA (4 h), and membrane/cytoskeletal fractions were analyzed by Western blotting to monitor redistribution of CLASP2. Equal protein amounts of corresponding total cell lysates were loaded and additionally probed for CLASP2 to ensure equal input protein. The results of Western blot analysis (right panel) confirm the expression of cell membrane (VEGFR2 and Na+/K+-ATPase) and cytosolic (HSP90 and GAPDH) protein markers in the corresponding fractions. C, cells were challenged with HKSA (4 h) with or without pretreatment with TubA, and co-immunoprecipitation was performed with p120 antibody followed by immunoblotting with CLASP2. The membrane was reprobed with p120 antibody to ensure even pulldown among the groups. Bar graphs depict a quantitative analysis of Western blotting densitometry data. Results are shown as mean ± S.D. n = 5; *, p < 0.05. Veh, vehicle.