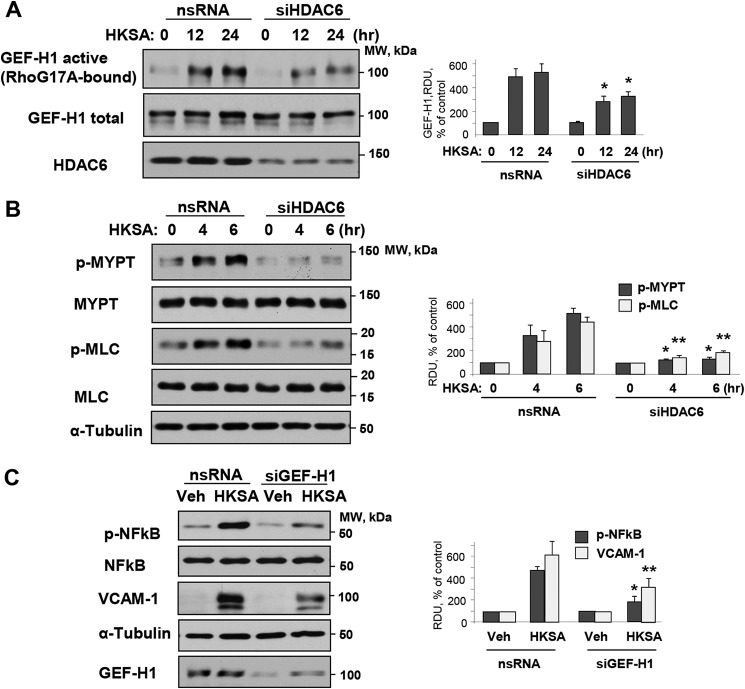
Figure 7.
MT-bound GEF-H1 dependent Rho activation mediates HKSA-induced EC barrier disruption and inflammation. HPAEC transfected with HDAC6-specific (siHDAC6) or nonspecific siRNA (nsRNA) were exposed to HKSA for the indicated times. A, a GEF-H1 activation assay was performed with RhoG17A beads, and active GEF-H1 captured by the beads were detected by Western blotting. The efficiency of HDAC6 knockdown was confirmed by Western blotting of total cell lysates with HDAC6 antibody. B, phosphorylation of MLC and myosin phosphatase (MYPT) in total cell lysates was detected by Western blotting with corresponding phosphospecific antibodies. Membranes were then reprobed with pan-MYPT (p-MYT) and pan-MLC (p-MLC) antibodies. C, HPAEC were transfected with GEF-H1–specific or nonspecific siRNA and challenged with HKSA 72 h after transfection. The levels of phospho-NF-κB (HKSA 6 h) and VCAM-1 (HKSA 24 h) were evaluated by Western blotting. Equal total protein amounts were loaded on each lane; probing with α-tubulin was used as a confirmatory normalization control. Bar graphs depict a quantitative analysis of Western blotting densitometry data and shown as mean ± S.D. n = 5; *, p < 0.05. Veh, vehicle.