Figure 8.
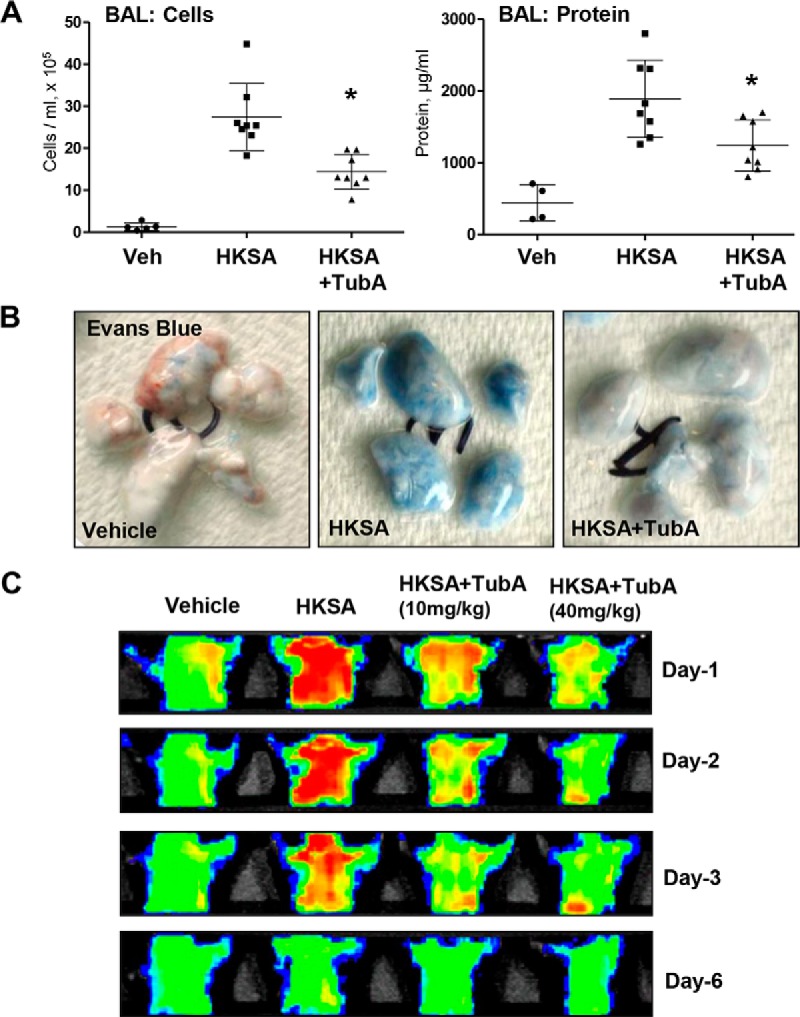
HDAC6 inhibition prevents HKSA-induced vascular leak and lung inflammation in vivo. Anesthetized mice were injected with HKSA (intratracheally, 2 × 108 bacterial cells/mouse) followed by intravenous injection of TubA. A, total cells and the protein content in BAL were determined 24 h after HKSA administration. n = 8; *, p < 0.05. Veh, vehicle. B, analysis of Evans Blue–labeled albumin extravasation into the lung parenchyma reflecting vascular leak. Lungs were excised from the chest, perfused with PBS, and imaged. Shown are representative single-animal images from three independent experiments. Nine total animals/condition were analyzed. C, live imaging analysis of lung vascular barrier dysfunction after HKSA intratracheal injection with and without intravenous administration of the indicated doses of TubA. HKSA-induced accumulation of fluorescent Angiosense 680 EX imaging agent in the lungs of the same animals was detected using the Xenogen IVIS 200 Spectrum imaging system at 1, 2, 3, and 6 days after HKSA challenge and presented in arbitrary colors. Shown are representative single-animal images from three independent experiments. Nine total animals/condition were analyzed.
