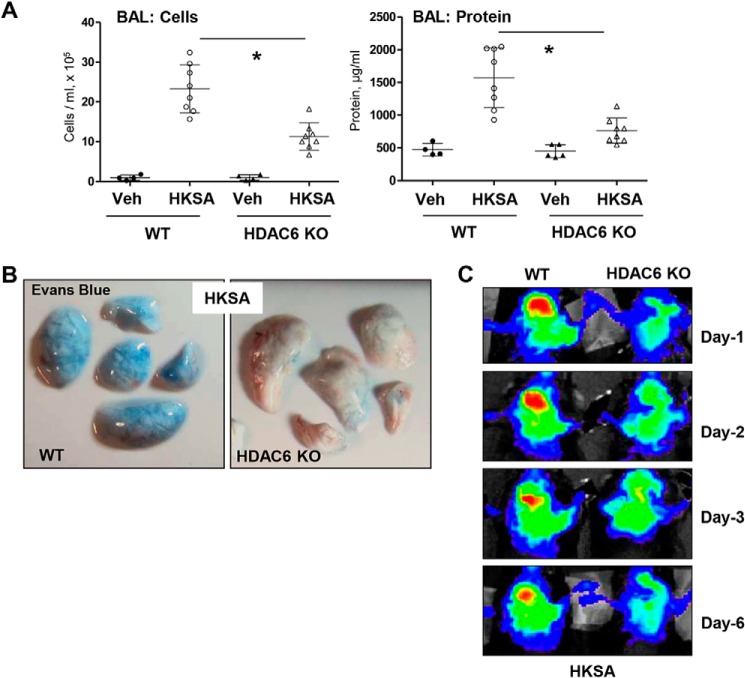
Figure 9.
HKSA-induced lung inflammation is attenuated in HDAC6 knockout mice. WT C57BL/6 or HDAC6 KO mice were exposed to HKSA (2 × 108 bacterial cells/mouse, intratracheally) for 24 h. A, BAL was collected, and total cells and protein content were determined 24 h after HKSA administration. HDAC6 KO mice showed a significant decrease in protein content and cell counts in BAL. n = 8; *, p < 0.05. Veh, vehicle. B, analysis of Evans Blue–labeled albumin extravasation into the lung parenchyma. Lungs from HKSA-challenged (24 h) WT and HDAC6 KO mice were excised from the chest, perfused with PBS, and imaged. Shown are representative single-animal images from three independent experiments. Six total animals/condition were analyzed. C, live imaging analysis of lung vascular barrier dysfunction after HKSA intratracheal injection in WT and HDAC6 KO mice. HKSA-induced accumulation of fluorescent Angiosense 680 EX imaging agent in the lungs of the same animals was detected using a Xenogen IVIS 200 Spectrum imaging system at 1, 2, 3, and 6 days after HKSA challenge and presented in arbitrary colors. Shown are representative single-animal images from three independent experiments. Six total animals/condition were analyzed.