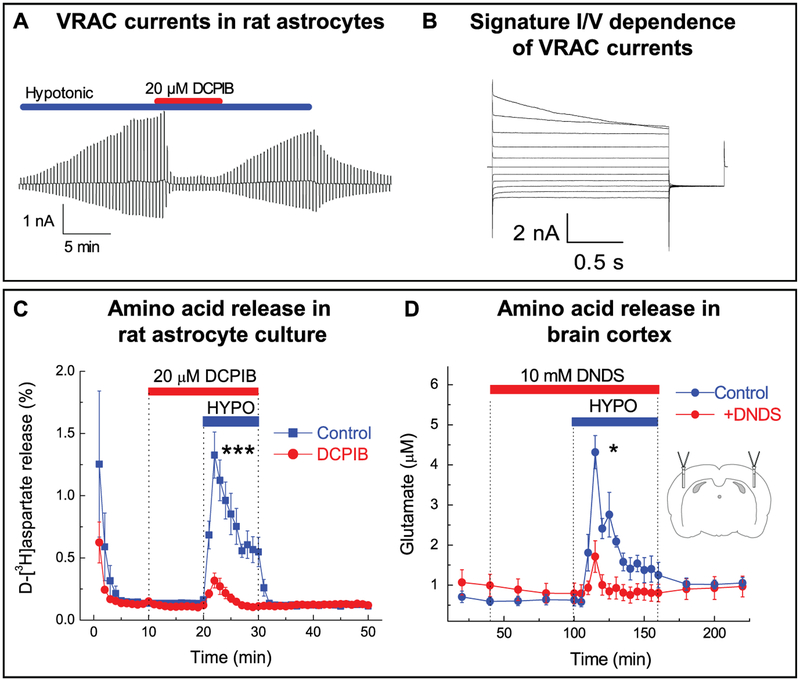
Figure 12.2.
Swelling-activated Cl− currents and amino acid release through VRAC in vitro and in vivo. (A) Representative whole-cell recordings of Cl− currents in primary rat astrocytes exposed to hypoosmotic medium (−60 mOsm). Activity of Cl− channels was measured by holding cells at 0 mV and alternately administering ± 40 mV voltage pulses. Currents were inhibited by treatment with the VRAC blocker DCPIB (20 μm). (B) Swelling-activated Cl− currents in astrocytes in response to 20 mV step pulses from −100 to +100 mV, displaying the characteristic outward rectification and time-dependent inactivation at positive potentials. (C) Effect of DCPIB on swelling-activated glutamate release in primary astrocytes, traced with the non-metabolizable glutamate analog D-[3H]aspartate. ***p < 0.001, effect of DCPIB. (D) Effect of the non-specific VRAC blocker DNDS on swelling-activated glutamate release in the rat cortex after stimulation with hypoosmotic artificial cerebrospinal fluid, measured by microdialysis approach and analyzed with HPLC. *p <0.05, effect of DNDS. (A-C) adapted from I.F. Abdullaev et al. (2006), with permission. (D) Reproduced from R.E. Haskew-Layton et al., 2008, under the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.