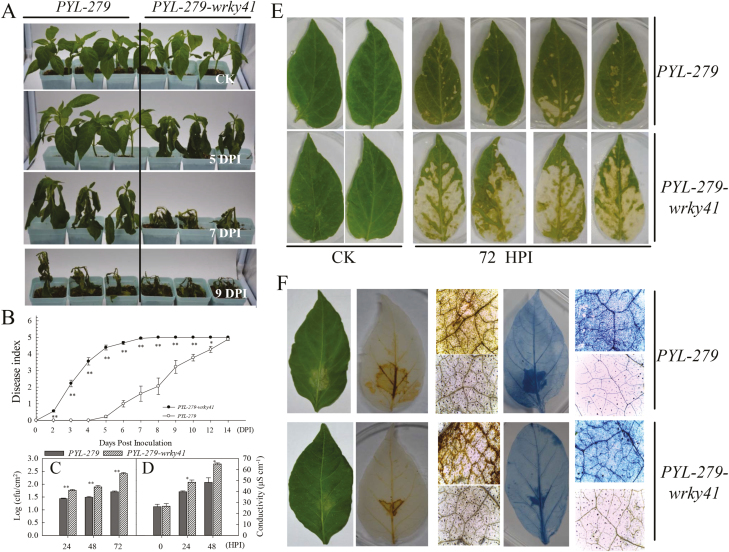
Fig. 8.
CaWRKY41 silencing enhances susceptibility to Ralstonia solanacearum FJ150501. (A) Appearance of PYL-279 and PYL-279-wrky41 pepper plants at 0, 5, 7, and 9 days post inoculation (DPI) with R. solanacearum. (B) Disease index scored daily for R. solanacearum-inoculated PYL-279 and PYL-279-wrky41 pepper plants. (C) Bacterial growth and (D) conductivity (as a measure of electrolyte leakage) in PYL-279 and PYL-279-wrky41 pepper leaves following R. solanacearum inoculation. HPI, hours post inoculation. Data represent the mean ±SE of three biological replicates. Asterisks indicate significant differences compared with control plants (Student’s t-test; *P<0.05, **P<0.01). (E) Effect of R. solanacearum on leaves isolated from PYL-279 and PYL-279-wrky41 plants. R. solanacearum was collected from stem exudates or the vascular portions of infected pepper leaves, and the appearance of symptoms was observed 72 HPI. CK, control untreated. (F) Decreased H2O2 levels and cell death in the leaves of PYL-279-wrky41 pepper plants compared with PYL-279 24 h after inoculation with R. solanacearum.