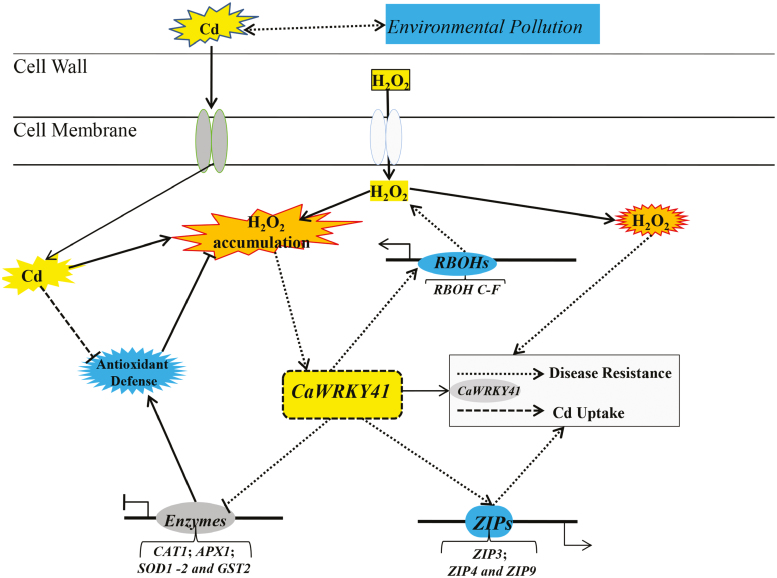
Fig. 9.
Working model for the role of CaWRKY41 in regulating Cd sensitivity and R. solanacearum resistance in pepper. Cd toxicity induces H2O2 production and inhibits the activity of ROS-scavenging enzymes, leading to accumulation of H2O2 and up-regulation of CaWRKY41. Subsequently, CaWRKY41 directly or indirectly activates the expression of ROS-producing genes (RBOH C-F) and Zn transporters (ZIP3, ZIP5, and ZIP9), and inhibits the expression of ROS-scavenging enzymes (CAT1, APX1, SOD1, SOD2, and GST2). Finally, a positive feedback loop between H2O2 accumulation and CaWRKY41 up-regulation coordinates the responses of pepper to R. solanacearum infection and Cd toxicity.