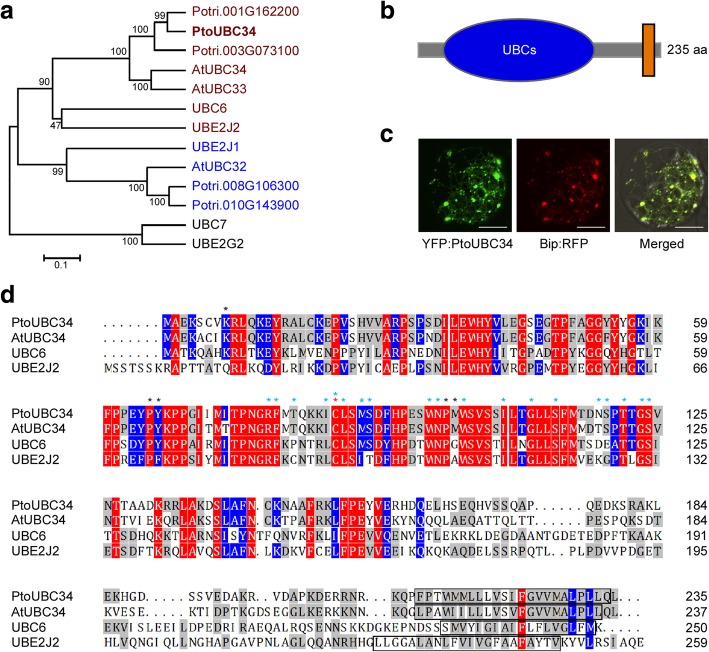
Fig. 2.
Characteristics of PtoUBC34. a. Phylogenetic analysis of PtoUBC34 and other ERAD-related UBC proteins in yeast (UBC6 and UBC7), humans (UBE2J1, UBE2J2, and UBE2G2), poplar, and Arabidopsis. The phylogenetic tree was established with full-length protein sequences by the neighbor-joining method. The bootstrap values out of 500 retrials are indicated at each branch. The scale (0.1) represents a 10% change in sequences. b. Schematic of PtoUBC34. The UBCc domain (blue) and a transmembrane domain (orange) are predicted in PtoUBC34 at the N-terminus and the C-terminus, respectively. c. Subcellular localizatin of PtoUBC34. PtoUBC34 was fused with YFP and co-transformed with the ER marker BiP:RFP [57] into P. tomentosa protoplasts. d. Multiple sequence alignment of yeast UBC6, human UBE2J2, Arabidopsis UBC34 and P. tomentosa UBC34. The conserved active Cys residue with red star, E3 interaction residues with black stars and Ub thioester intermediate interaction residues with blue stars are indicated. The transmembrane regions are shown in boxes. Bar in (c) = 10 μm