FIG 1.
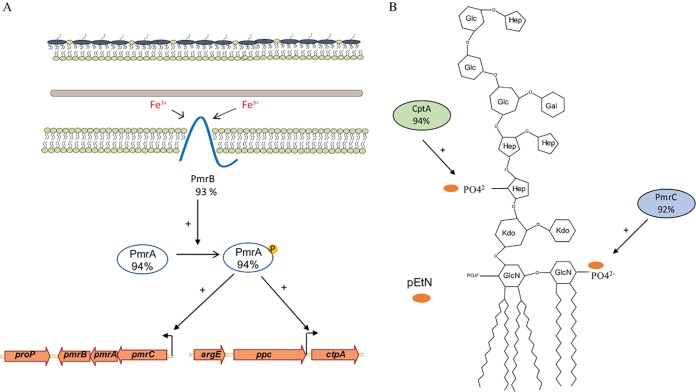
PmrAB regulates pmrC (eptA) and cptA in C. rodentium. (A) Model representing the PmrAB TCS. Under conditions of high Fe3+, the cytoplasmic PmrA response regulator becomes phosphorylated and active, resulting in differential expression of several genes, including pmrC (eptA) and cptA (31). (B) Schema showing PmrC (EptA) and CptA-mediated modifications of LPS. In E. coli, PmrC (EptA) and CptA add pEtN groups to the lipid A and core regions of LPS, respectively (36). Percentages refer to the similarity of the PmrA, PmrC (EptA), and CptA proteins between E. coli and C. rodentium.