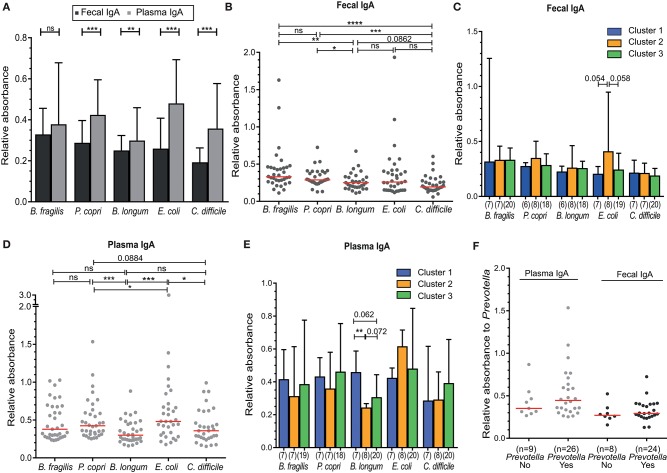
Figure 4.
Higher IgA reactivity in plasma compared to feces against indicator microbiota organisms, but lack of a significant association to microbiota Cluster. (A) Fecal and plasma IgA binding against the indicator intestinal microbiota microorganisms—Bacteroides fragilis, Prevotella copri, Bifidobacterium longum, Escherichia coli, and Clostridium difficile. (B) Fecal IgA reactivity of all individuals, or (C) between Cluster 1–3 separately. (D) Plasma IgA reactivity of all individuals, or (E) between Clusters 1–3 separately. (F) Plasma and fecal IgA binding to Prevotella copri for individuals containing Prevotella (Yes) or not (No) in their intestinal microbiota. IgA binding for all experiments shown was measured as absorbance at 450 nm relative to a positive control (25 ng/ml IgA isolated from human colostrum, Sigma). Significance was determined using the Wilcoxon matched-paired signed rank test (A) or Mann-Whitney U test (B,C). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001. Data represent all 35 included volunteers, which are only separated into cluster in panels (C,E) (cluster 1, n = 7; cluster 2, n = 8; cluster 3, n = 20).