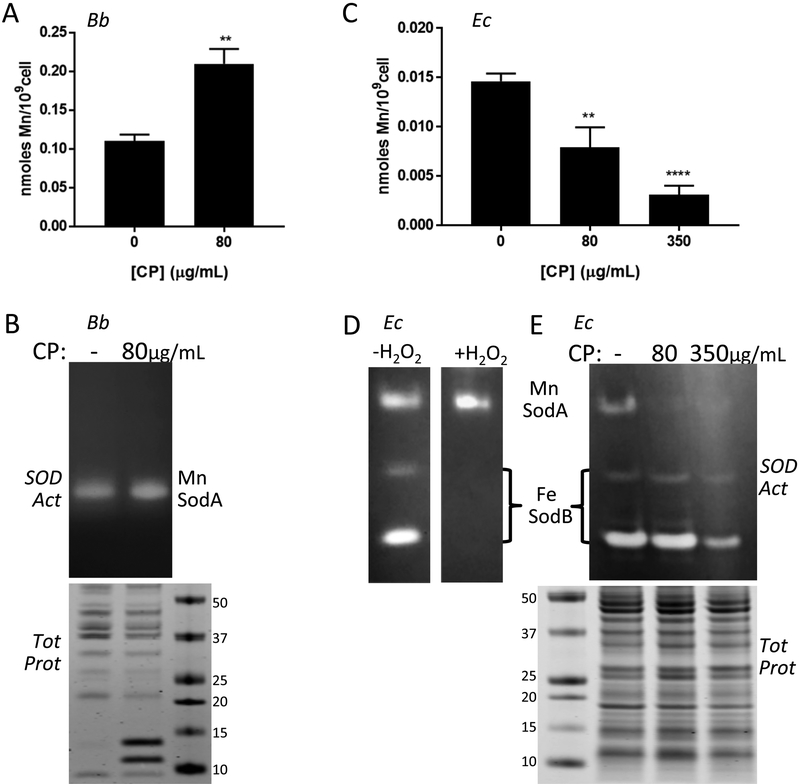
Fig. 7.
Effects of CP on Mn requiring SodA and total cellular Mn in Bb versus E. coli. Bb (A, B) and E. coli cells (“Ec” C-E) were grown in BSK II supplemented with the designated concentrations of CP. (A,C) Mn levels were measured in Bb (A) or E. coli (C) cells by ICP-MS. Results are averages of at least five (A) and four (C) replicates over three experimental trials, **p ≤ 0.0035, ****p < 0.0001, where CP treated samples are compared to no CP controls. Error bars are standard error. (B,D,E) Whole cell lysates were analyzed for SOD enzymatic activity by native gel electrophoresis and NBT staining (B top, D, E top). Denaturing gel electrophoresis and coomassie staining (B bottom, E bottom) were used as a loading control. The positions of SodA and SodB on the native gels are indicated; numbers represent molecular weight markers. Results are representative of five (B) and three (E) experimental trials. (D) The native gel was treated with H2O2 where indicated to inactivate Fe containing SodB prior to NBT staining, as described in Experimental.