Figure 1.
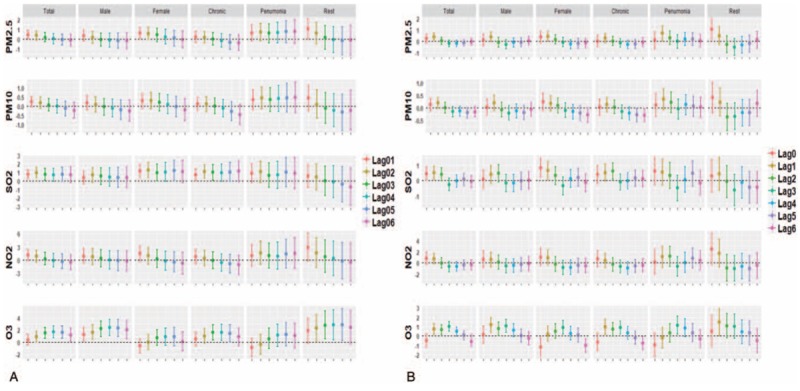
The excess risk and 95% CI per 10 μg/m3 increase of air pollutants on cause-specific daily deaths using single pollutant models at lag 0 to 7 day and lag 01 to 06 day in Jinan, China from 2011 to 2017. Results were controlled for seasonality, day of the week, temperature, relative humidity, air pressure, and wind speed. A. lag effects; B. cumulative effects. Chronic refers to chronic airway diseases (J40–47) including COPD, asthma, chronic respiratory failure, bronchiectasis. Pneumonia refers to J12–J18. Rest refers to J30–39 and J60–J99 including interstitial pneumonia and other respiratory diseases. Diseases are classified according to the International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision (ICD-10; WHO 1993). Statistically significant (∗P < .1, ∗∗P < .05, ∗∗∗P < .01). CI = confidence interval, COPD = chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases, NO2 = nitrogen dioxide, O3 = ozone, PM = particulate matter, PM10 = particulate matter with an aerodynamic diameter of b10 μm, PM2.5 = particulate matter with an aerodynamic diameter of b2.5 μm, SO2 = sulfur dioxide.
