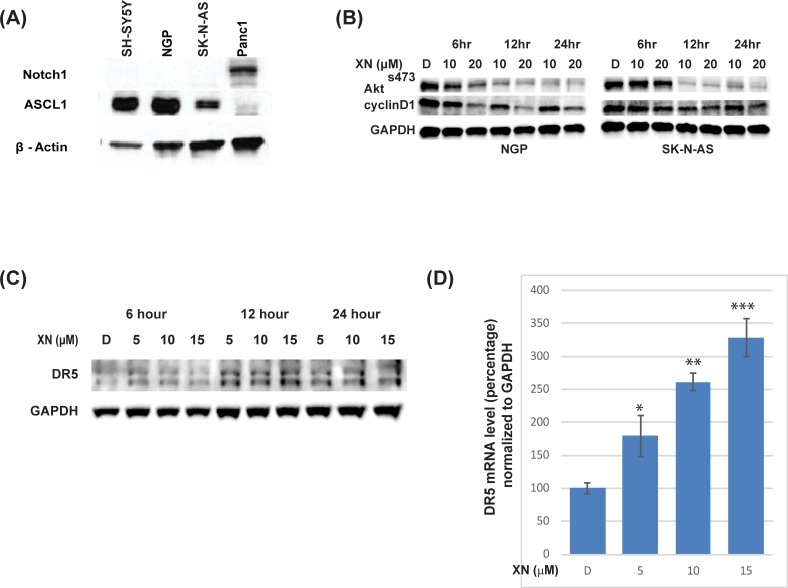
Fig 4. XN regulates the Akt pathway and associated with an increase in DR5 expression.
A. Notch signaling is minimally active in NGP, SK-N-AS, and SH-SY-5Y, as evidenced by minimal expression of Notch intracellular Domain1, whereas there is increased expression of achaete-scute complex-like1 (ASCL1), a downstream target of Notch signaling. B. Inhibition of Akt pathway by XN treatment was observed by reduction in phosphorylation of Akt (ser473) as early as 6 hrs. This was associated with a reduction in CyclinD1. C. NB cell line, SK-N-AS was treated with indicated concentrations of XN for 6–24 hours’ time points and lysates were prepared. Western blot analysis of the lysates shows a time-dependent increase in DR5 expression following XN treatment. GAPDH was used as loading control. D. DR5 gene expression increases with XN treatment in a dose-dependent fashion in quantitative RT PCR analysis. GAPDH was used as a control and for normalization. * p<0.05; ** p<0.01; *** p<0.001.