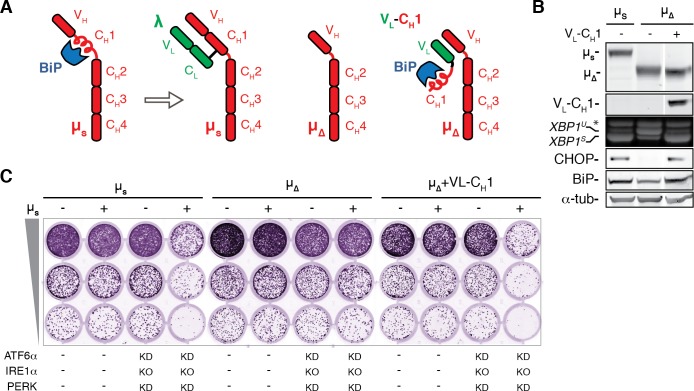
Figure 7. The BiP-sequestering CH1 domain of µs is necessary and sufficient to cause UPR activation and proteotoxic ER stress in absence of the UPR.
(A) Schematic representation of BiP associating with the CH1 domain of µs until it is displaced by the light chain (λ). Deletion of the CH1 domain (µ∆) abolishes BiP association, but through pairing of the VH and VL domains, the CH1 domain can associate in trans by virtue of a synthetic chimeric VL-CH1 construct. (B) HeLa cells were induced for 24 hr with 0.5 nM Mif to express the transgenes µs, µs∆CH1 (µ∆) alone or in conjunction with VL-CH1, as indicated. Immunoblotting of lysates revealed levels of µs, µ∆, VL-CH1, BiP, CHOP, and α-tubulin, as in Figure 1A. (C) Growth assay as in Figure 1A of HeLa cells inducibly expressing µs, µs∆CH1 (µ∆) in conjunction with VL-CH1 or not, and in which the UPR was ablated (i.e. IRE1α was deleted (KO), and ATF6α and PERK were silenced in combination), or not, as indicated.