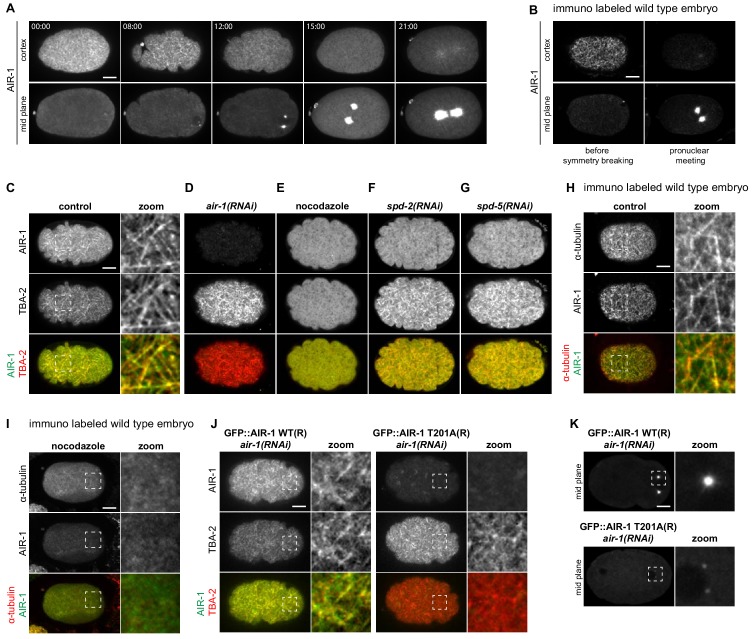
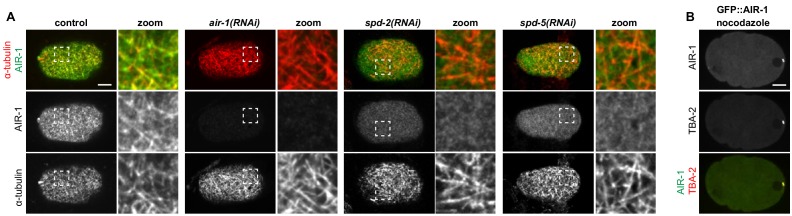
Figure 5. AIR-1 localizes to cortical microtubules.
(A) Time lapse microscopy of an embryo expressing endogenously tagged GFP::AIR-1. Upper panels: maximum z-projection of 1.5 µm of the cortical planes. Lower panels: maximum z-projection of 7.5 µm of the middle planes of the same embryo. A representative embryo out of 9 that were imaged is shown. (B) Wild-type embryos fixed and stained for endogenous AIR-1 before symmetry breaking (left panels) and at pronuclear meeting (right panels). Upper panels: cortical plane; lower panels: middle plane of the same embryo. (C–F) Cortical images of embryos expressing endogenously tagged GFP::AIR-1 (green) and mCh::TBA-2 (red) prior to symmetry breaking; embryos were depleted by RNAi of AIR-1 (D), SPD-2 (F) or SPD-5 (G), or else treated with nocodazole to depolymarize microtubules (E). Depletion of AIR-1 (D), SPD-2 (F) or SPD-5 (G) by RNAi, and depletion of microtubules by nocodazole (E). The zoom highlights co-localization of GFP::AIR-1 with mCh::TBA-2 in the control condition. (H,I) Cortical images of wild-type (H) or nocodazole-treated (I) embryo fixed and stained for α-tubulin and AIR-1. The zoomed regions highlight co-localization of endogenous AIR-1 with microtubules in the control condition. (J) Embryos prior to symmetry breaking expressing GFP::AIR-1 WT or GFP::AIR-1 T201A (RNAi-resistant, denoted R) (green) and mCh::TBA-2 (red) and depleted of endogenous AIR-1 using RNAi. The zoomed regions highlight co-localization of α-tubulin and AIR-1 solely in the case of the wild type transgenic construct. Only the cortical plane is shown. (K) Cortical images of embryos expressing GFP::AIR-1 WT or GFP::AIR-1 T201A (RNAi resistant, denoted R) (green) and mCh::TBA-2 (red) at the onset of pronuclear migration. air-1(RNAi) is directed against endogenous AIR-1. (C–K) Representative images are shown out of >10 embryos analyzed for each condition.