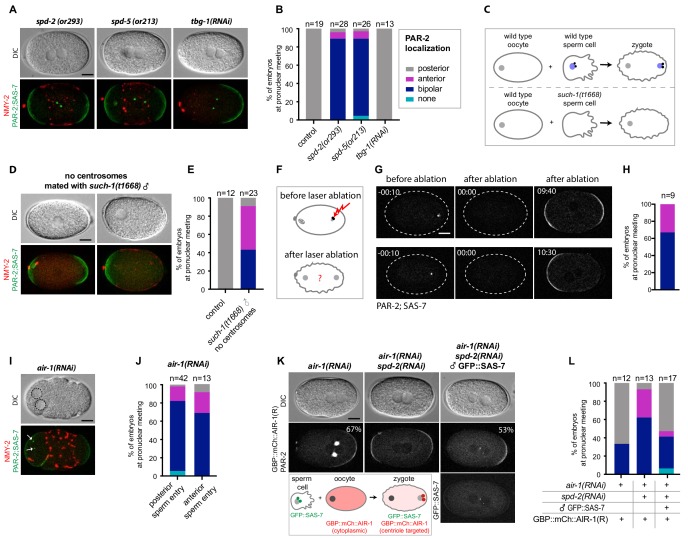
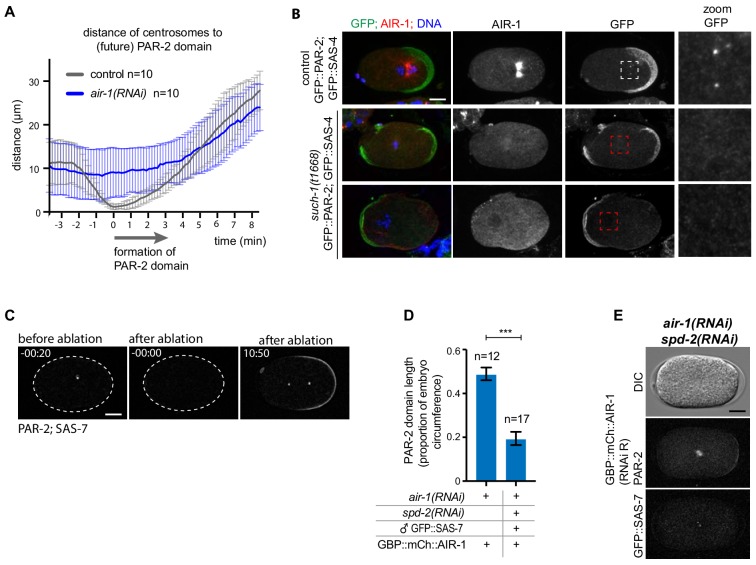
Figure 7. Centrosomes ensure uniqueness of symmetry breaking in C.elegans zygotes.
(A) spd-2(or293), spd-5(or213) or tbg-1(RNAi) embryos, as indicated, expressing RFP::NMY-2 (red), GFP::PAR-2 and GFP::SAS-7 (both green). Upper panels: DIC, lower panels: grey scale. (B) Quantification of GFP::PAR-2 distributions corresponding to (A). (C) Schematic showing experimental set up for (D) and (E). (D) fem-1(hc17) hermaphrodites expressing RFP::NMY-2 (red), GFP::PAR-2 and GFP::SAS-7 (both green) mated with such-1(t1668) males. Note lack of male pronucleus and of centriolar GFP::SAS-7. (E) Quantification of GFP::PAR-2 distributions corresponding to (D). (F) Schematic illustrating the experimental set-up of the centrosome laser ablation experiments. (G) Two embryos expressing GFP::PAR-2 and GFP::SAS-7 prior to laser ablation (t=-00:10), immediately after laser ablation of the centrosome (t = 00:00) and at pronuclear meeting (t = 09:40 and t = 10:30). (H) Quantification of GFP::PAR-2 distributions corresponding to (G). (I) air-1(RNAi) embryo expressing RFP::NMY-2 (red), GFP::PAR-2 and GFP::SAS-7 (both green) with sperm entry next to the maternal pronucleus. Dotted lines: pronuclei; arrows: centrosomes. (J) Quantification of GFP::PAR-2 distributions in air-1(RNAi) embryos with sperm entry next to maternal pronucleus ("anterior") or opposite from it ("posterior"). (K) Embryos expressing GBP::mCh::AIR-1 (RNAi-resistant, denoted R) and mCh::PAR-2, depleted of endogenous AIR-1 either alone (left panel) or together with SPD-2 (middle panel). Right panel: hermaphrodites depleted of endogenous AIR-1 and SPD-2 were mated with GFP::SAS-7 males; see schematic for a description of the experimental set up. Note that GBP::mCh::AIR-1(R) is not cortical in embryos depleted of SPD-2. (L) Quantification of mCh::PAR-2 distributions corresponding to (K).