Fig. 6. Activation of LHb TRPV1 channels contributes to anxiety- and depression-like behaviors.
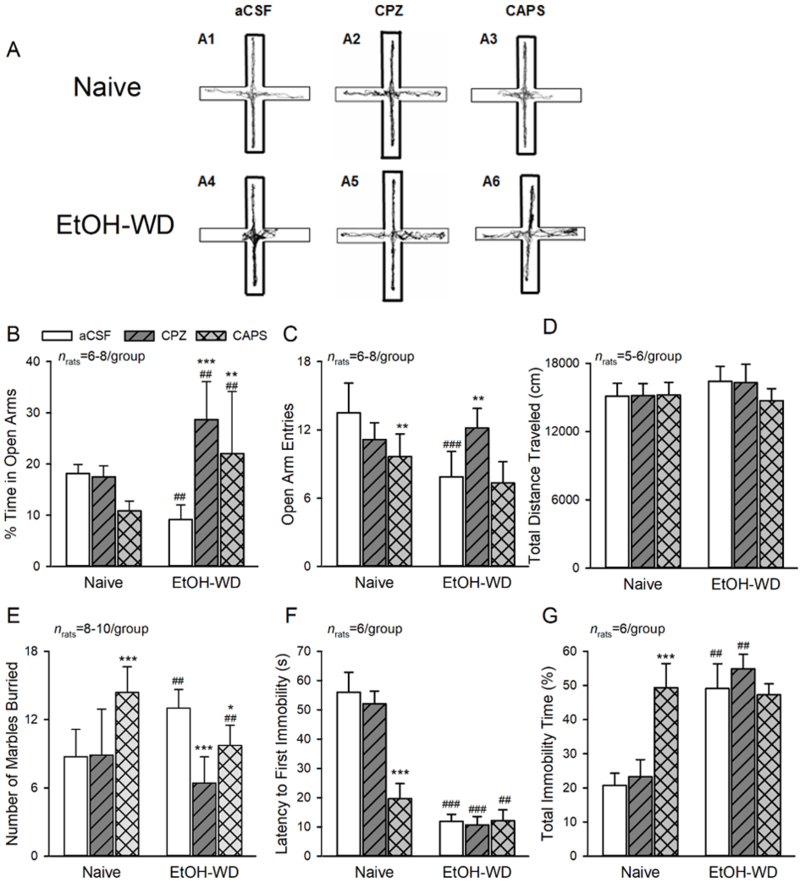
(A-D) Elevated Plus Maze (EPM) Data. (A1, A4) Representative traces show EtOH-WD rats spend less time in open arms compared to Naive rats. In Naïve rats, intra-LHb either capsazepine (CPZ, A2) or capsaicin (CAPS, A3), did not alter the time in (B), and the entries (C) to the open arms. In EtOH-WD rats, CPZ (A5) or CAPS (A6) significantly increased open arm time (B). (D) The total distance traveled in the EPM was not changed. (E) In the marble burying test, EtOH-WD rats buried significantly more marbles than Naïve rats. In Naïve rats, CAPS increased the marbles buried; in EtOH-WD rats, CPZ or CAPS significantly decreased the marbles buried. (F, G), In the forced swimming test, EtOH-WD rats had a significantly shorter latency to first immobility (F) and longer total immobility time (G) compared to naïve rats. CPZ did not alter the latency or total immobility time, while CAPS significantly reduced the latency and increase the immobility time in Naïve rats. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 relative to respective aCSF. ##P < 0.01, ###P < 0.001, Naïve in comparison with EtOH-WD rats. Data were analyzed with two-way ANOVA and Tukey post hoc comparison.
