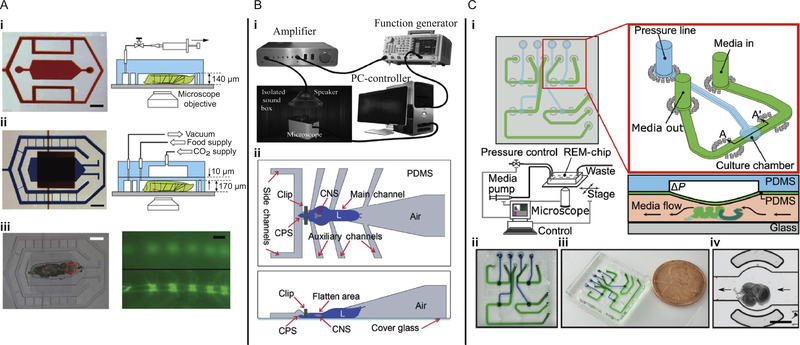
FIG. 6.
Microfluidic devices for mechanobiology of Drosophila melanogaster combine mechanical stimulation with imaging. (A) Photographs and schematics of microfluidic devices for (i) short- and (ii) long-term immobilization of larvae for studying cellular responses to neural injuries (scale bars 1 mm). (iii) Bright-field (left, scale bar 1 mm) and fluorescent images (right, scale bar 20 μm) of the larva body with a fluorescently (GFP) labeled ventral cord. (B) (i) Experimental setup for examining the auditory response of fruit fly larvae. (ii) Schematic top and side views of the FlexiChip used to immobilize larvae for quick manual animal loading. (C) Regulated Environment for Microorgans (REM) chip, (i) schematic design of the chip with the inset showing detail of a single chamber unit, and the operation diagram for wing disc compression, (ii) and (iii) photographs of the device with individual fluidic (green) and pressure (blue) channels, and (iv) wing disc loaded into a culture chamber of the device (scale bar 400 μm).
Panel (A) reproduced and adapted from reference Ghannad-Rezaie, M., Wang, X., Mishra, B., Collins, C., & Chronis, N. (2012). Microfluidic chips for in vivo imaging of cellular responses to neural injury in Drosophila larvae. PLoS ONE, 7(1), e29869. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0029869 with permission from PloS ONE under the CC BY licensel; Panel (B) reproduced and adapted from reference Ghaemi, R., Rezai, P., Iyengar, B. G., & Selvaganapathy, P. R. (2015). Microfluidic devices for imaging neurological response of Drosophila melanogaster larva to auditory stimulus. Lab on a Chip, 15(4), 1116–1122. http://xlink.rsc.org/?DOI=C4LC01245C. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4LC01245C with permission from the Royal Society of Chemistry under the CC BY license; Panel (C) reproduced and adapted from reference Narciso, C. E., Contento, N. M., Storey, T. J., Hoelzle, D. J., & Zartman, J. J. (2017). Release of applied mechanical loading stimulates intercellular calcium waves in Drosophila wing discs. Biophysical Journal, 113(2), 491–501. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0006349517306264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bpj.2017.05.051 with permission from Elsevier.