Figure 5.
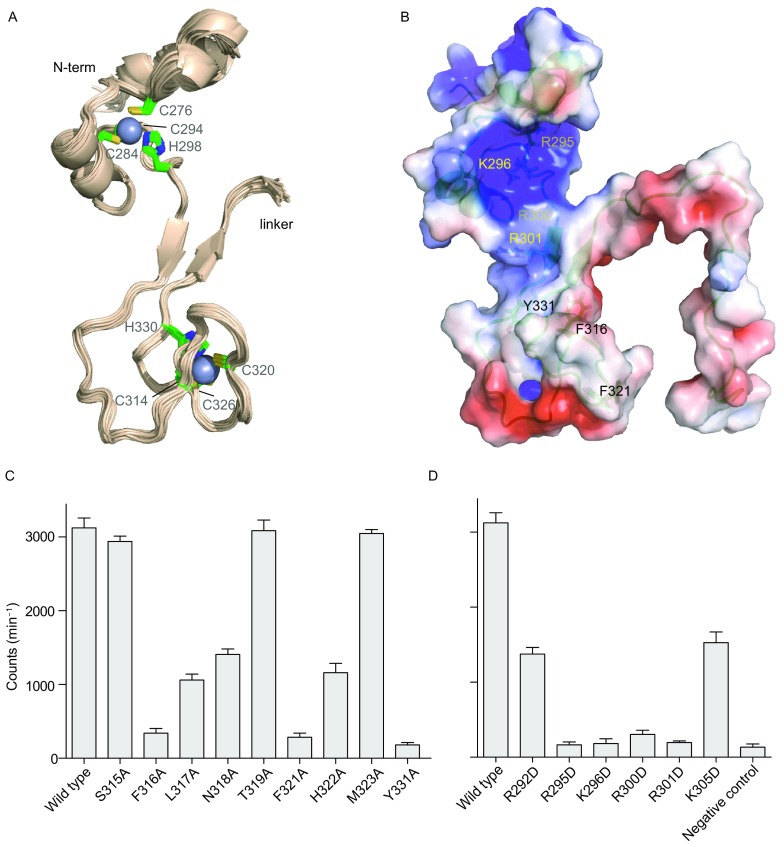
Solution structure of METTL3 ZFD. (A) Superposition of 25 lowest-energy structures of the ZFD. The structures were superimposed by backbone heavy atoms for residues 276–336, and the last 20 flexible residues are not shown. Zn2+ ions are shown as spheres, and the coordinating residues are shown as sticks. (B) Electrostatic potential colored surface, on a scale from red (−3 kT/e) to blue (+4 kT/e), with the functionally important basic residues (yellow labels) and hydrophobic residues (black labels) denoted. (C) Methyltransferase activities for the METTL3-METTL14 heterodimers harboring point mutations to the hydrophobic residues. (D) Methyltransferase activities for the METTL3-METTL14 heterodimers harboring point mutations to the basic residues. Negative control (NC) was assessed for an RNA containing 5′-GGGCU-3′ instead of 5′-GGACU-3′ consensus sequence. The average counts per minute (±SD with n = 3) are reported
