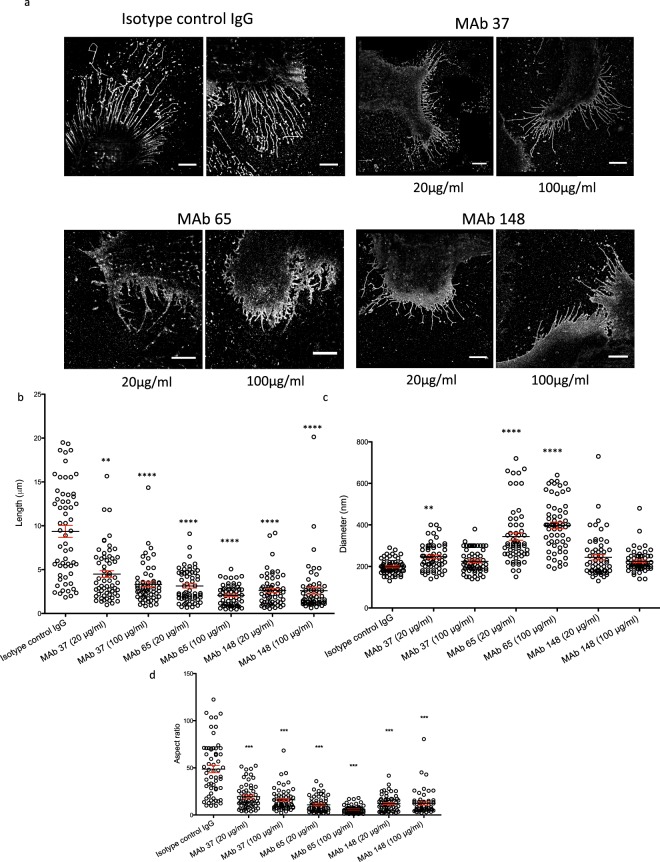
Figure 4.
Super-resolution microscopy analysis shows inhibition of filament formation by M2e-specific IgGs (n = 60). MDCK cells were seeded in 8 well microslides, treated with M2e-speficic MAb 37 (IgG1), MAb 65 (IgG2a), MAb 148 (IgG1), or isotype control IgG1 + IgG2a at 20 or 100 μg/mL and then infected with A/Udorn/72 at MOI 5 and incubated for 24 Hrs at 37 °C in serum-free medium. The cells were then washed with PBS and fixed with 2% PFA at room temperature for 20 min. Infected cells and A/Udorn/72 filaments were visualized by immune-staining with polyclonal convalescent mouse serum directed against A/Udorn/72, followed by Alexa Fluor 647 Donkey Anti-Mouse IgG serum (a) STORM images of MDCK cells infected with influenza and treated with different MAb at different concentrations (20 µg/ml and 100 µg/ml). (b) Representation of the length (µm) of all filaments quantified (n = 60) from infected cells and treated with MAb. (c) Representation of width (diameter (nm)) of filaments quantified (n = 60). (d) Representation of the aspect ratio (length/diameter) of all filaments quantified (n = 60). Bar = 5 µm. The length of A/Udorn/72 filaments was significantly reduced in M2e-specific MAb treated cells (B). The experiments were performed in triplicate wells for each condition and repeated at least three times with similar results. One-way ANOVA. Non-significant (ns), **p ≤ 0.01; ***p ≤ 0.001; ****p ≤ 0.0001.