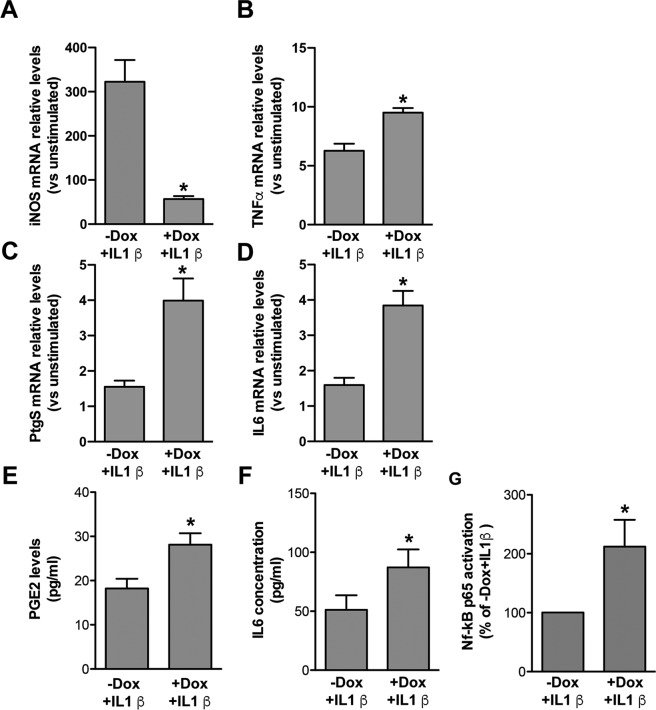
Figure 2.
Regulation of inflammatory genes and related proteins/metabolites in IL1β-activated murine WT-FUS overexpressing astrocytes and relative controls, and determination of NF-kB p65 activation. (A–D) RT PCR analyses of iNOS (A), TNFα (Β), PTGS2 (C) and IL6 (D) mRNA expression upon IL1β stimulation in cultures treated or not with Dox, relative to unstimulated cells (−Dox − IL1β). Data show that TNFα (Β), PTGS2 (C) and IL6 (D) mRNA relative expression upon IL1β stimulation is higher, and that of iNOS (A) lower, in cells overexpressing WT-FUS (+Dox + IL1β), compared to non-overexpressing cells (−Dox + IL1β). Data are means ± SEM, n = 3–6, *P < 0.05 vs. −Dox + IL1β. (E,F) PGE2 and IL6 were quantified by EIA and ELISA assays, respectively, in the conditioned media collected from astrocyte-like cells differentiated in the presence or in the absence of Dox for 6 days and stimulated in the last 24 hrs with IL1β. In accordance with gene expression data, PGE2 and IL6 levels were higher in cells overexpressing WT-FUS (+Dox + IL1β) than in non-overexpressing cells (−Dox + IL1β). Data are means ± SEM, n = 3, *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.005 vs. −Dox + IL1β; (G) NF-kB p65 activation, assessed by NFkB p65 ELISA-based kit on whole cell lysates, was increased in astrocyte-like cells overexpressing WT-FUS and treated with IL1β for 45 min before collection (+Dox + IL1β). Data are expressed as the percentage of activation respect to control cells (−Dox + IL1β) and are means ± SEM, n = 5, *P < 0.05.