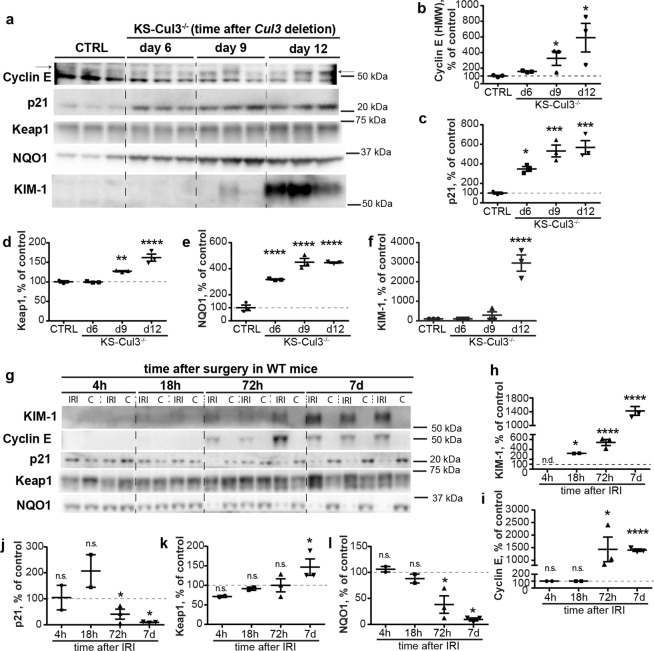
Figure 2.
Cul3 deletion and IRI have differential effects on cell cycle proteins and Keap-1/Nrf2 signaling. (a–f) Western blot analysis showed increased abundance of cyclin E and its inhibitor p21, as well as Keap1 and NQO1, a readout of Nrf2 signaling activation, after 6 or 9 days in kidney-specific Cullin 3 knockout (KS-Cul3−/−) mice. KIM-1 signal was not detectable in control mice or 6 days after induction of Cul3 deletion, and appeared at day 9 and 12 after Cul3 disruption (f). (g–i) Compared to contralateral control kidney, Western blotting of wild-type kidney lysates revealed increased KIM-1 abundance 18 h after ischemia-reperfusion injury (IRI) (g,h), followed by increased abundance of cyclin E 72 h after IRI (g,i). (g–l) In contrast to KS-Cul3−/− mice, KIM-1 induction was associated with decreased abundance of p21 (g,j), and increased Keap1 and decreased NQO1 (consistent with lower Nrf2 activity) after 72 h of IRI (g,k,l). Mean values are shown ± SEM. In (b-f, n = 3) asterisks show significant differences between control and each KS-Cul3−/− mice group obtained from ordinary one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test, with a single pooled variance. In (h-l, n = 2–3), protein abundance in injured kidney was compared to its contralateral control kidney using paired t-test for each time point. *P ≤ 0.05, **P ≤ 0.01, ***P ≤ 0.001, ****P ≤ 0.0001; Abbreviations: n.s., not significant; n.d., not detectable. Coomassie-stained gels used for Western blot normalization can be found in Supplementary Fig. S4. Western blots were cropped for clarity; uncropped images can be found in Supplementary Figs S5–S7.