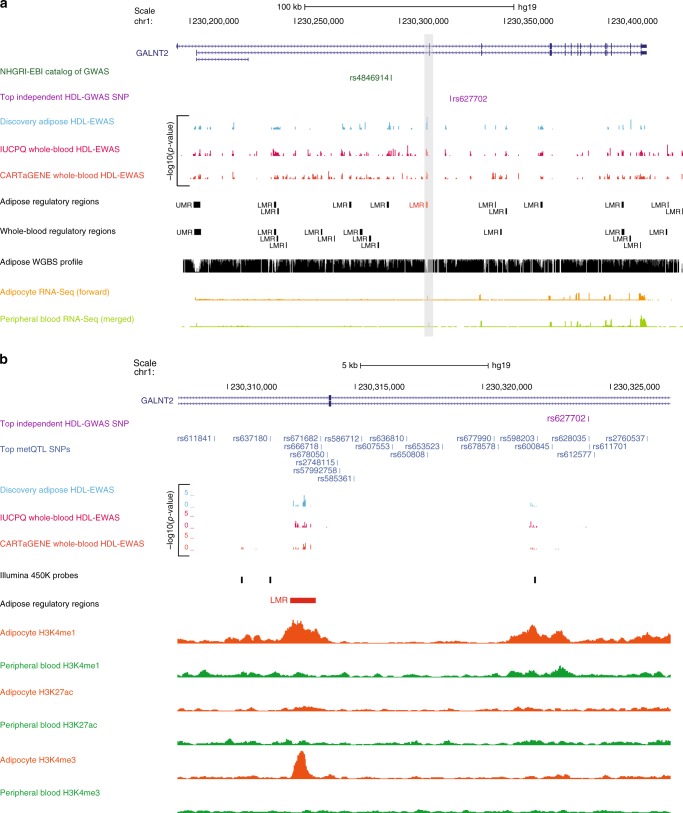
Fig. 4.
HDL-C linked adipose-specific regulatory region under genetic regulation. A discovery HDL-CpG (chr1:230313001; corrected p = 2.0 × 10−5; sky blue track) maps within an intragenic region of GALNT2 (chr1:230312462-230313455) overlapping an adipose-specific putative enhancer region (LMR; shown in red in a the broad and b zoomed-in view). The adipose-specific nature of the epigenetic signature at this locus is supported by patterns in adipocyte nuclei (Roadmap Epigenomics Consortium; donor 92 for H3K4me1 and H3K4me3; donor 7 for H3K27ac; orange tracks) versus peripheral blood (Roadmap Epigenomics Consortium; donor TC015; green tracks) chromatin marks as well as from intersecting whole-blood EWAS signals (pink and dark orange tracks). We show that the enhancer region is under extensive genetic regulation by nearby cis-SNPs (gray blue tracks in b) that are in high LD (r2 > 0.9) with an HDL-linked GWAS SNP (Global Lipids Consortium; rs627702; p = 5.0 × 10−24; purple tracks), which is independent of the previously reported top HDL-linked SNP at this locus (rs4846914; p = 4.0 × 10−41; dark green track in a). We depict a lack of coverage of the 450 K array at this region. Adipocyte-specific (in-house data; light orange track) and peripheral blood RNA-Seq (Roadmap Epigenomics Consortium; donor TC014; light green track) data at the locus is also depicted in a