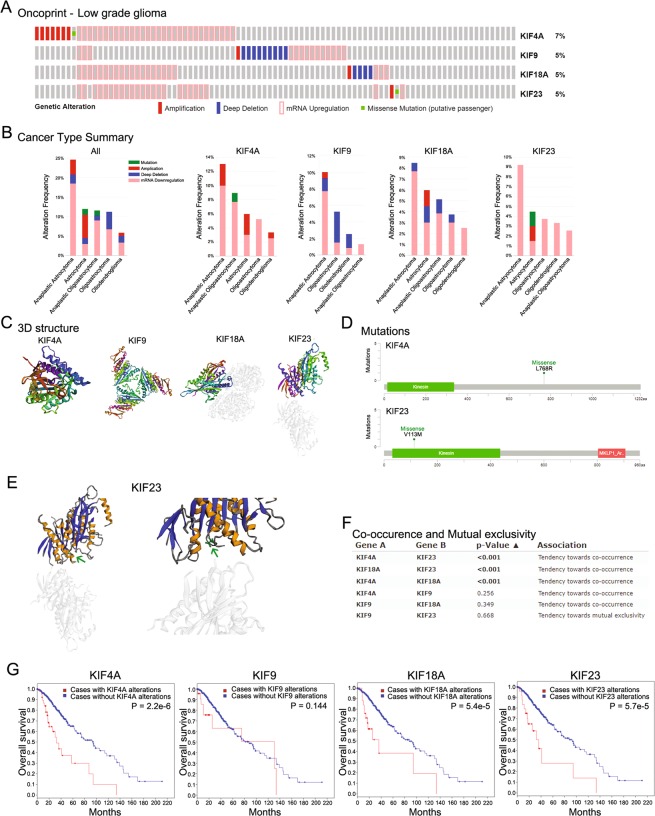
Figure 2.
Genomic analysis of KIF4A, 9, 18A, and 23 in LGG. (A) The oncoprints of KIF4A, 9 18A, and 23 were identified. Genetic alterations of KIF4A, 9, 18A, and 23. The column represents LGG patients, and the row represents gene alterations, including amplification, deep deletion, mRNA upregulation, and missense mutation. (B) Genetic alterations summarized according to cancer type of LGG. (C) The 3D crystal structure of KIF4A, 9, 18AA, and 23 is shown in rainbow colors (from N- to C- terminal ends). (D) The mutations of KIF4A and 23 were plotted. The kinesin motor domain is displayed in green with 15–336 amino acids. In the 768 amino acid sequence of KIF4A, Leucine was changed to Arginine. In the 133 amino acid sequence of KIF23, Valine was changed to Methionine. (E) The 3D structure of KIF23 implemented with missense mutations was plotted. In the kinesin motor domain of KIF23, the mutated part was marked with a green arrow. (F) Co-occurrence and mutual exclusivity were examined with KIF4A, 9, 18A, and 23. (G) Kaplan–Meier survival analysis of KIF4A, 9, 18A, and 23 was conducted with and without gene alterations. The p-value for Kaplan–Meier curves was calculated using the log-rank test.