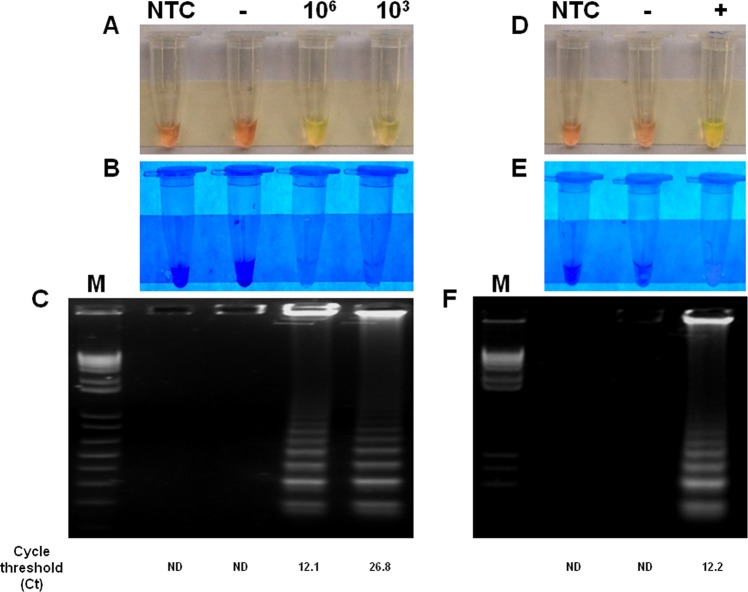
Figure 1.
Detection of ZIKV in virus-spiked mosquito samples and crude lysate of experimentally infected Aedes aegypti. Crude lysates of uninfected A. aegypti were spiked with ZIKV to result in either a high (1 × 106 PFU/mL) or low viral load (1 × 103 PFU/mL) and processed for RT-LAMP without RNA isolation (A–C). (D–F) Represents RT-LAMP results of experimentally infected mosquitoes. RT-LAMP amplicons were observed by visual color change of the products and gel electrophoresis. The amplification products were observed by naked eye under natural light (A,D), under UV irradiation (B,E) and agarose gel electrophoresis (C,F). Legends in (A–C) are: NTC (non-template control): water; (−): macerate of uninfected Aedes aegypti; (106): macerate of Aedes aegypti spiked with 106 PFU; (103): macerate of Aedes aegypti spiked with 103 PFU. Legends in (D–F) are: NTC (non-template control): water; (−): macerate of uninfected Aedes aegypti; (+):macerate of Aedes aegypti experimentally infected with ZIKV. M: molecular weight marker.