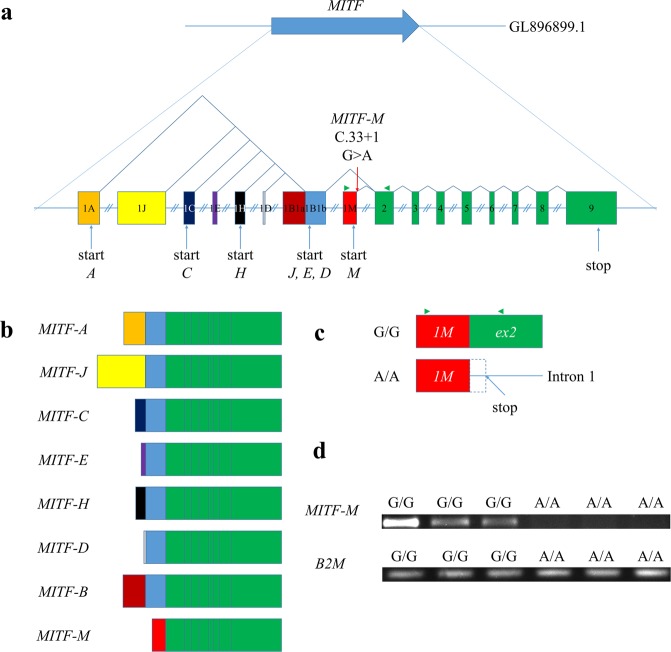
Figure 3.
Effects of MITFh mutation on transcripts of the MITF M-isoform. (a) Structure of mink MITF gene. Coloured boxes indicated exons 1 A (orange), 1 J (yellow), 1 C (dark blue), 1E (purple), 1 H (black), 1D (grey), 1B1a (brown), 1B1b (blue), 1 M (red) Green boxes indicate exons 2–9, common to all isoforms. Exons 1 A, 1 J, 1 C, 1E, 1 H, 1D, 1B1a and 1 M were predicted in silico. Green triangle indicates primers used for RT-PCR. Equal introns sizes are shown for simplification. (b) Structure of in silico predicted mink MITF isoforms (expression of MITF-M mRNA was confirmed with RT-PCR). Each isoform, except M, has a unique promoter and a first exon followed by 1B1b and 2–9 exons. The M-isoform is specific to melanocytes and melanoma cells, it does not include exon 1B1b. (c) Effect of MITFh mutation on MITF-M transcript. This mutation potentially retains the first intron in cDNA and introduces a stop codon after position 51 of the intron (indicated as dotted box). The end product is a truncated 29 polypeptide containing only the first 11 amino acids of MITF-M. Green triangle indicates primers used for RT-PCR. (d) Agarose gel electrophoresis of MITF-M cDNA 1M-2 exons and B2M cDNA 1–2 exons. No MITF-M cDNA 1–2 exons were observed in the cortex of Hedlund white (h/h) minks, which were homozygous for this mutation.