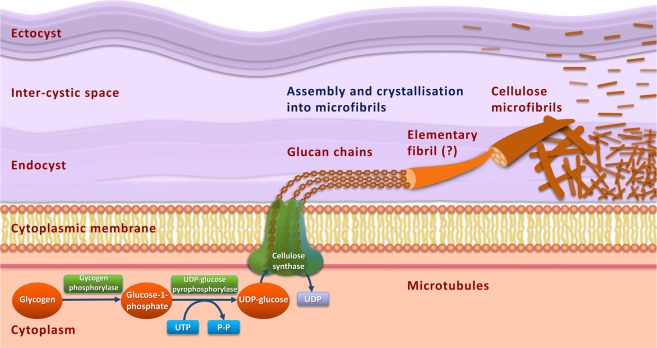
Figure 9.
Hypothetical model for the biosynthesis of cellulose in Acanthamoeba cyst. Glycogen in the cytoplasm is degraded by catalytic action of glycogen phosphorylase, releasing glucose-1-phosphate. Subsequently, UDP (uridine diphosphate) glucose is synthesised from glucose-1-phosphate and UTP (uridine triphosphate) catalysed by UDP-glucose pyrophosphorylase. Through the action of cellulose synthase the glucose residues are polymerized into individual glucan chains that are translocated across the cytoplasmic membrane. The interaction of the cellulose synthase with microtubules is strongly supposed. Glucan chains are likely assembled into elementary fibrils that are associated into microfibrils. This process is called crystallisation. For simplicity, the number of glucan chains is schematic.