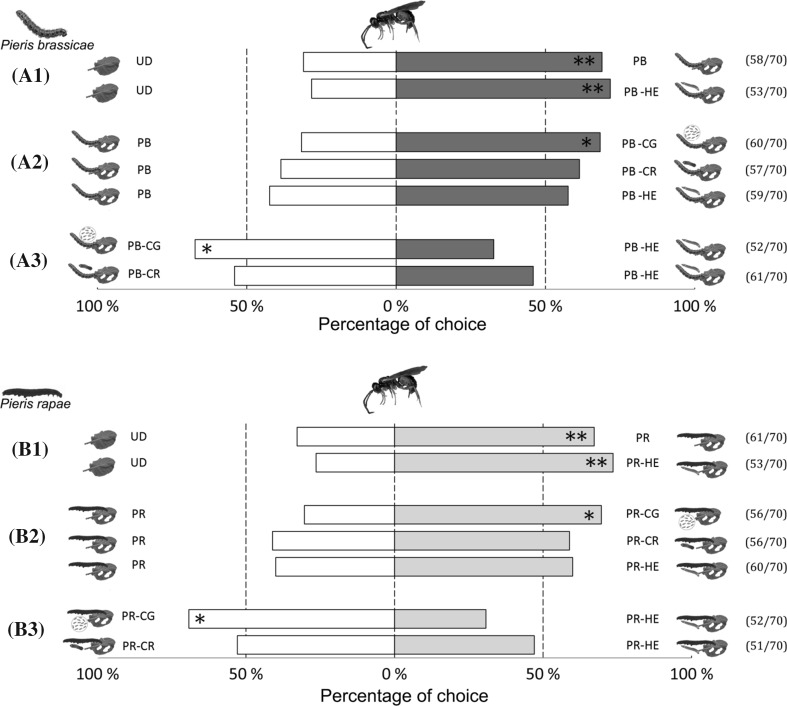
Fig. 2.
Preference of Lysibia nana females for herbivore-induced plant volatiles (HIPVs) in two-choice olfactometer tests. Above: olfactometer tests using Pieris brassicae as herbivore species comparing undamaged control plants (UD), P. brassicae-damaged plants (PB), plants damaged by Hyposoter ebeninus-parasitized P. brassicae caterpillars (PB-HE), plants damaged by Cotesia glomerata-parasitized P. brassicae caterpillars (PB-CG), plants damaged by Cotesia rubecula-parasitized P. brassicae caterpillars (PB-CR). Below: olfactometer tests using Pieris rapae as herbivore species comparing undamaged control plants (UD), P. rapae-damaged plants (PR), plants damaged by Hyposoter ebeninus-parasitized P. rapae caterpillars (PR-HE), plants damaged by Cotesia glomerata-parasitized P. rapae caterpillars (PR-CG), plants damaged by Cotesia rubecula-parasitized P. rapae caterpillars (PR-CR). Asterisks indicate a preference which is significantly different from a 50:50 distribution within a choice test (GLM, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01). Numbers between brackets indicate the number of responding wasps vs. the total number of wasps tested