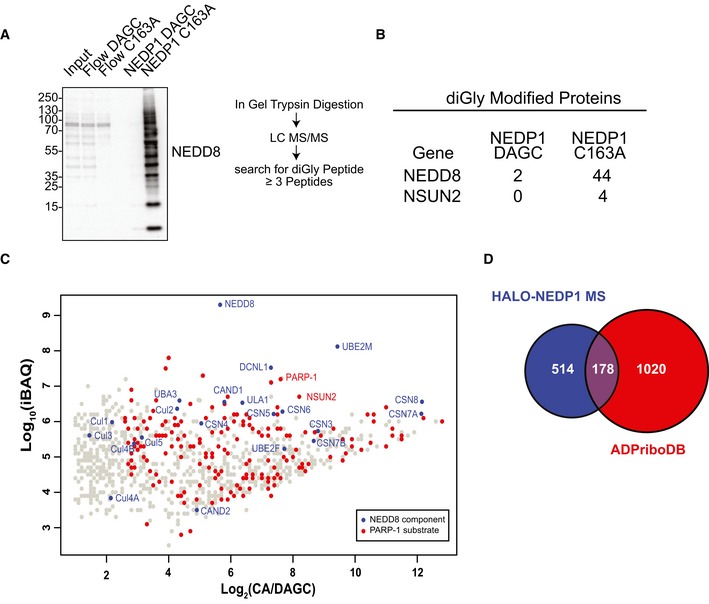
Scatter plot of proteins identified by mass spectrometry analysis identifies NEDD8 and components of the NEDD8 conjugation pathway as being the most abundant proteins in HEK 293 NEDP1 KO lysates following NEDP1‐CA pulldown. iBAQ analysis of proteins identified in (A) is plotted as the log
2 value of the enrichment ratio (mass spectrometry intensity of the HALO‐NEDP1 CA pulldown over HALO‐NEDP1 DAGC pulldown) versus the log
10 value of the iBAQ intensity from the HALO‐NEDP1 CA pulldown. Blue markers indicate known components of the NEDD8 pathway, and red markers indicate proteins that have been identified as substrates of PARP‐1 in the database of ADP‐ribosylated proteins, ADPriboDB (Vivelo
et al,
2017).