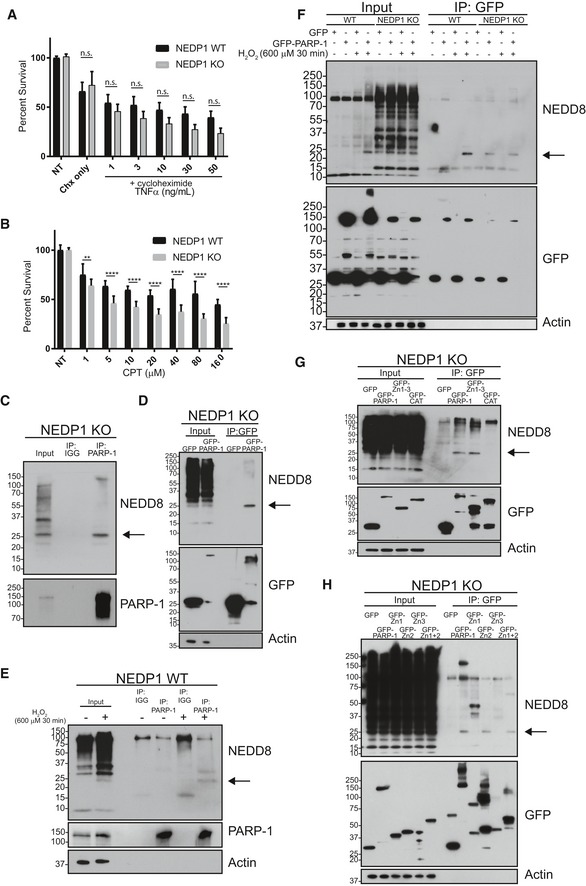
NEDP1 KO U2OS cells are not resistant to induction of apoptosis from combined treatment with TNF‐α and cycloheximide. U2OS cells were plated in 96‐well plates and incubated with cycloheximide (10 μg/ml) before addition of the indicated amount of TNF‐α. Cell survival was determined 24 h later using the CellTiter‐Glo assay. Graphs represent the mean ± SEM of the percent survival compared to untreated cells. Two‐way ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc test: n = 3, n.s. denotes not statistically significant.
NEDP1 KO U2OS cells are not resistant to treatment with camptothecin (CPT). WT U2OS and NEDP1 KO cells were plated in 96‐well plates and treated with the indicated amount of CPT. Forty‐eight hours after exposure cell survival was measured using the CellTiter‐Glo assay. Graphs represent the mean ± SEM of the percent survival compared to untreated cells. Two‐way ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc test: n = 3, **P < 0.0021, ****P < 0.0001.
NEDD8 trimers co‐immunoprecipitate with endogenous PARP‐1 in NEDP1 KO cells. Lysates were prepared from U2OS NEDP1 KO cells, and immunoprecipitation was performed with PARP‐1‐Trap or GFP‐Trap as a negative control. Bound proteins were resolved by SDS–PAGE and processed for Western blot analysis with the indicated antibodies.
NEDD8 trimers bind to GFP‐PARP‐1. U2OS NEDP1 KO cells were transfected with GFP or with GFP‐PARP‐1, and 24 h later, cell lysates were collected. Immunoprecipitation was then performed with GFP‐Trap, and bound proteins were resolved by SDS–PAGE and processed for Western blot analysis with the indicated antibodies. GFP‐PARP‐1 but not GFP alone can co‐immunoprecipitate NEDD8 trimers from NEDP1 KO cells.
NEDD8 trimers form in WT U2OS cells after treatment with H2O2 and co‐immunoprecipitate with endogenous PARP‐1 but not with immunoglobulin control (IGG). WT U2OS cells were left untreated or treated with H2O2 (600 μM) for 30 min and were harvested for immunoprecipitation and Western blot analysis as in (C).
NEDD8 trimers bind to GFP‐PARP‐1. WT or U2OS NEDP1 KO cells were transfected with GFP or with full‐length GFP‐PARP‐1 and 24 h later treated as indicated with H2O2 (600 μM) for 30 min before cell lysates were collected. Immunoprecipitation was then performed with GFP‐Trap, and bound proteins were resolved by SDS–PAGE and processed for Western blot analysis with the indicated antibodies. GFP‐PARP‐1 but not GFP alone can co‐immunoprecipitate NEDD8 trimers from WT cells only after H2O2 treatment or from both treated or untreated NEDP1 KO cells.
NEDD8 trimers bind to the DNA‐binding domain of PARP‐1 (Zn1–3) but not to its automodification and catalytic domain (CAT). NEDP1 KO U2OS cells were transfected with GFP, GFP‐PARP‐1, GFP fused to the DNA‐binding domain of PARP‐1 (AA 1–336) or with GFP fused to the PARP‐1 automodification and catalytic domain (AA 336–1014). Twenty‐four hours post‐transfection, cell lysates were collected and immunoprecipitation with GFP‐Trap was performed. Bound proteins were eluted and resolved by SDS–PAGE analysis, followed by Western blot analysis with the indicated antibodies.
NEDD8 trimers specifically bind to the second zinc finger of PARP‐1. NEDP1 KO U2OS cells were transfected with GFP, GFP‐PARP‐1, or with GFP fused to the Zn1 domain (AA 1–96), the Zn2 domain (AA 97–215), the Zn3 domain (AA 216–336) or the Zn1 + 2 domains (AA 1–215) of PARP‐1. Twenty‐four hours post‐transfection, cell lysates were collected and immunoprecipitation with GFP‐Trap was performed. Bound proteins were eluted and resolved by SDS–PAGE analysis, followed by Western blot analysis with the indicated antibodies.