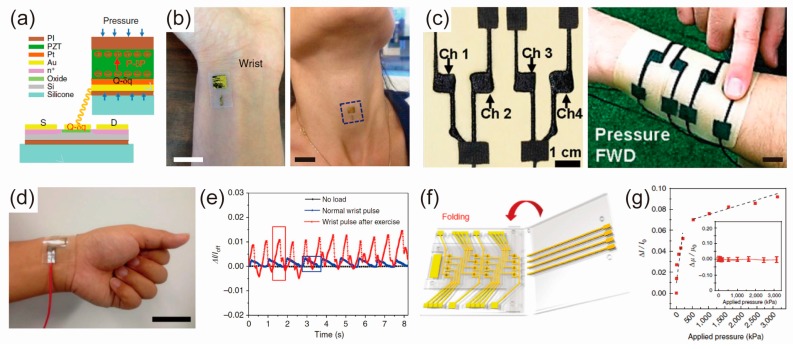
Figure 2.
Wearable pressure sensors. (a) Cross-sectional schematic illustration of the pressure sensor and its connections to an associated transistor. (b) Photograph of the pressure sensor placed on a wrist and neck for measuring fast transients in the blood pressure (scale bars 1 cm and 2 cm). Reprinted with permission from Ref. [3]. Copyright 2014, Nature Publishing Group. (c) Images of pressure sensor printed on the commercial elastomeric patch. The sensor array is composed of four channels of pressure sensors (scale bars 1 cm). Reprinted with permission from Ref. [39]. Copyright 2014, John Wiley and Sons. (d) Photograph showing the skin-attachable sensor directly above the artery of the wrist (scale bar 3 cm). (e) Measurement of the physical force of a heartbeat under normal and exercise conditions. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [36]. Copyright 2014, Nature Publishing Group. (f) Schematic image of pressure-sensitive graphene FETs with air-dielectric layers. (g) Plot of normalized drain current changes versus applied pressure. (inset indicates relative change in the field effect mobility under applied pressure). Reprinted with permission from Ref. [33]. Copyright 2017, Nature Publishing Group.