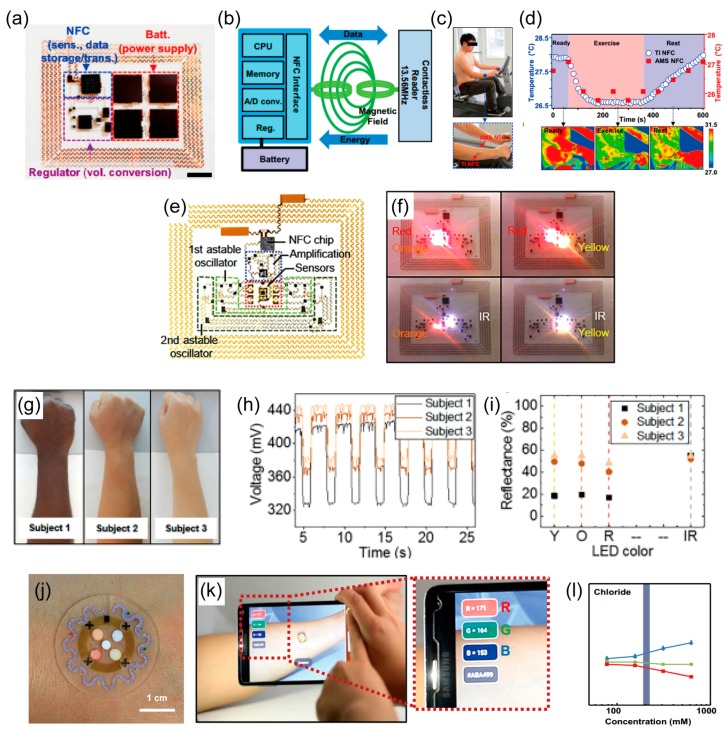
Figure 10.
Near field communication (NFC)-enabled wearable sensor. (a) Image of the NFC-enabled wearable sensor system composed of the NFC devices, batteries, and a power regulator. Scale bar, 5 mm; (b) Schematic illustration of the entire operation system; (c) Photo images of the NFC-enabled wearable sensor attached onto the human skin during exercise; (d) Temperature data and IR images at the stage of the before, during, and after exercise (which correspond to the “ready”, “exercise”, “rest”) recorded by using NFC-enabled wearable sensor with a battery module (AMS NFC, red squares) and with the battery-integrated system (TI NFC, open circle). (a–d) Reproduced with permission from Ref. [176]. Copyright 2016, National Academy of Sciences; (e) Image of a NFC-enabled wearable sensor system including four pulsed LEDs (red, IR, orange, and yellow), two oscillators, amplifier and sensors; (f) Photo images of the NFC-enabled wearable sensor system during operation; (g) Images of subjects with different skin colors; (h,i) Wirelessly measured data and calculated reflectance value of the different skin colors. (e–i) Reproduced with permission from Ref. [157]. Copyright 2016, American Association for the Advancement of Science; (j) Optical image of a fabricated device mounted on the forearm; (k) Pictures demonstrating NFC between a sweat monitoring device and a smartphone to launch software for image capture and analysis; (l) Standard calibration curves between normalized %RGB value and concentration of markers for quantitative analysis (error bars show s.d. (N = 3)). (j–l) Reproduced with permission from Ref. [177]. Copyright 2016, American Association for the Advancement of Science.