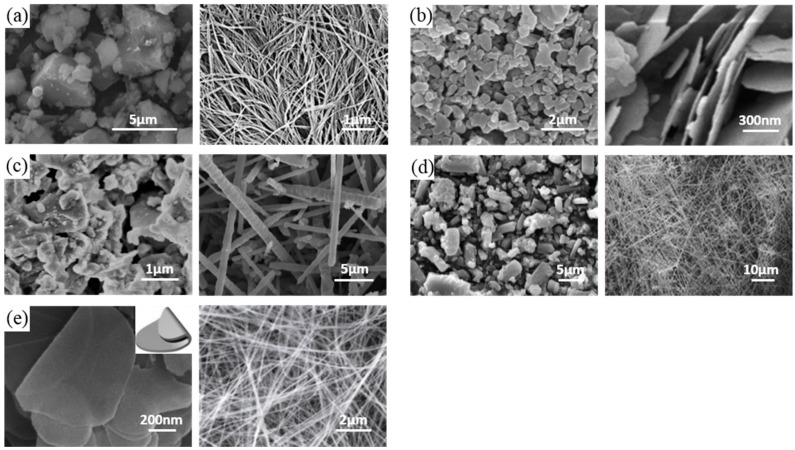
Figure 1.
Examples of several high thermal conductive nanoscale ceramic fillers. (a) Aluminum nitride (AlN) spherical particles and nanowires [8,9]. (b) Aluminum oxide (Al2O3) spherical particles and platelets [10,11]. (c) Silicon carbide (SiC) particles and whiskers [12,13]. (d) Silicon nitride (Si3N4) spherical particles and rods [3,14]. (e) Boron nitride (BN) plates and nanotubes [4,15]. {(a)(left): Reprinted with permission from [8] Copyright (2015) Elsevier. (a)(right): Reprinted with permission from [9] Copyright (2009) Springer. (b)(left): Reprinted with permission from [10] Copyright (2014) Elsevier. (b)(right): Reprinted with permission from [11] Copyright (2010) Royal Society of Chemistry. (c)(left): Reprinted with permission from [12] Copyright (2008) Elsevier. (c)(right): Reprinted with permission from [13] Copyright (2012) Elsevier. (d)(left): Reprinted with permission from [3] Copyright (2007) Elsevier. (d)(right): Reprinted with permission from [14] Copyright (2013) Royal Society of Chemistry. (e)(left): Reprinted with permission from [4] Copyright (2016) John Wiley and Sons. (e)(right): Reprinted with permission from [15] Copyright (2013) John Wiley and Sons}.