Figure 4.
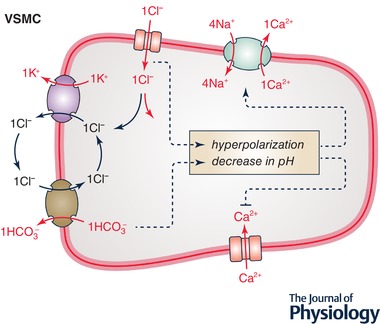
Role of K+‐Cl− cotransport in arterial VSMCs
Ion transport systems shown correspond to KCC3, Ca2+‐activated Cl− channel (CACC), SLC8A1 (Na+/Ca2+ exchanger or NCX type 1), L‐type voltage‐sensitive Ca2+ channel (Cav1) and SLC4A1 or SLC26A7. Increased KCC3 activity promotes Cl− entry (or decrease Cl− exit) through CACC and, secondarily, anion exchange by SLC4A1 or SLC26A7. It should therefore decrease membrane potential as well as intracellular pH, and thereby stimulate Na+/Ca2+ exchange by NCX1 and inhibit Ca2+ movement through Cav1. The end‐result of increased KCC3 activity should thus be a decrease in [Ca2+]i and, secondarily, in myogenic tone.
