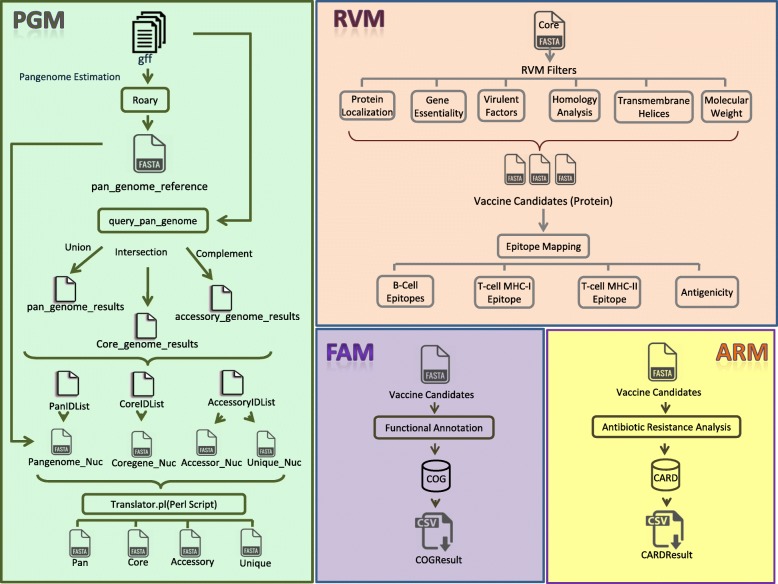
Fig. 1.
workflow of Pangenome-Reverse Vaccinology Package: Four modules of the pipeline (1) PGM (Pangenome Estimation Module), (2) RVM (Reverse Vaccinology Module), (3) FAM (Functional Annotation Module), (4) ARM (Antibiotic Resistance Association Module). PGM starts with multiple genomes files (.gff). These files are subjected to pangenome estimation pipeline (Roary), generating a pan_genome_reference along with several other supplementary files. Roary commands of query_pan_genome (union, intersection, complement) generate files (pan_genome_results, core_genome_results, accessory_genome_results). These files include gene ID (all isolates) in the respective category (Pan, Core, and Accessory) file. IDs lists (PanIDList, CoreIDList, AccessoryIDList) are picked from these files. IDs are then mapped to pan_genome_reference file and nucleotide FASTA sequences are extracted (Pangenome_Nuc, Coregene_Nuc, Accessor_Nuc, Unique_Nuc). Protein FASTA files (Pan, Core, Accessory, Unique) are generated by running a Perl script (Translator.pl). These predicted sets (Pan, Core, and Accessory) from PGM can be further subjected to RVM to identify putative vaccine candidates. Where selected pangenome category passes through each subfilter of RVM that extracts putative vaccine candidates along with their epitopes using the epitope mapping component. FAM and ARM identify functional annotation/significance and antibiotic resistance association of input FASTA file employing COG/UniProt and CARD databases, respectively. The results are displayed in CSV files