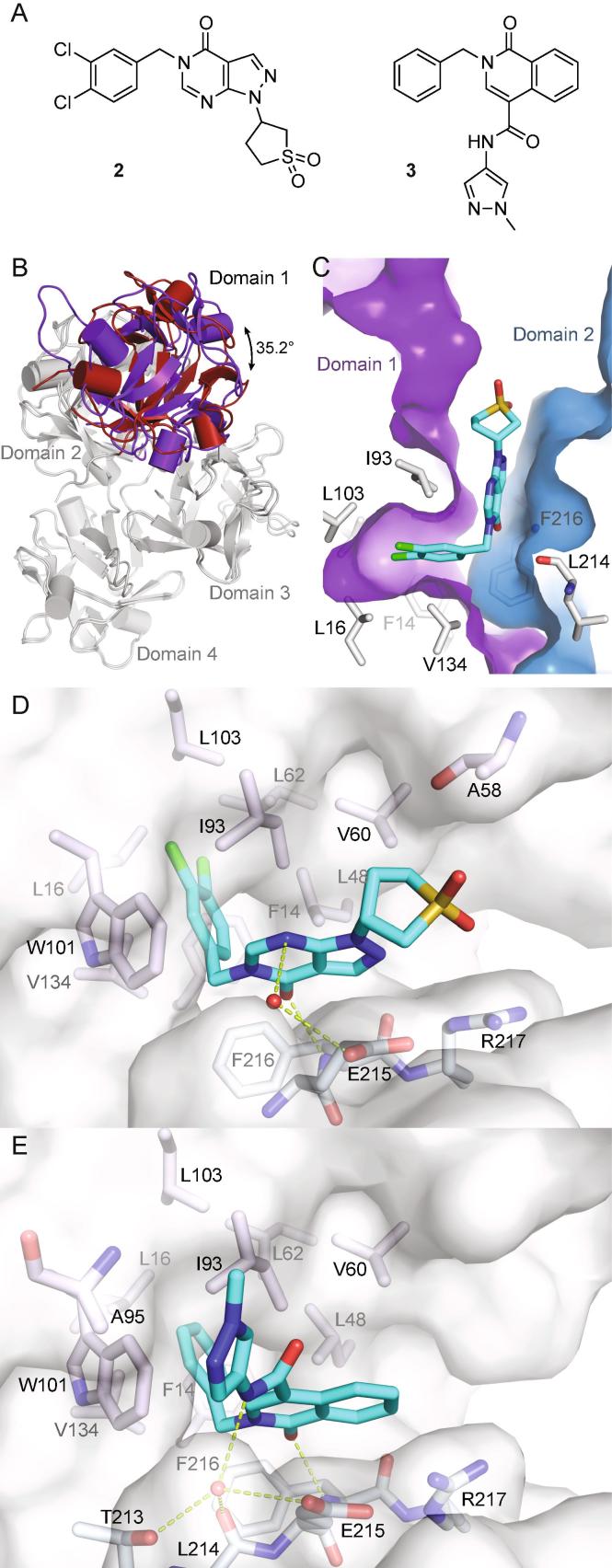
Fig. 2.
Fascin undergoes a significant conformational change upon binding of compounds 2 and 3. A) Chemical structures of 2 and 3. B) Apo-fascin (PDB id 3P53, red) and the fascin·2 complex (PDB id 6I10, purple) superimposed on the relatively rigid domains 2–4 (grey; RMSD = 1.1 Å for 348 Cα atoms), viewed along the domain 1 rotation axis. C) Compound 2 bound to fascin oriented as Fig. 1C/D (proteins superimposed on domain 1). D) Detail view of the fascin·2 complex. Conventions as in Fig. 1E, the red sphere represents a bound water molecule. E) Detailed view of the fascin·3 complex (PDB id 6I11). (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)