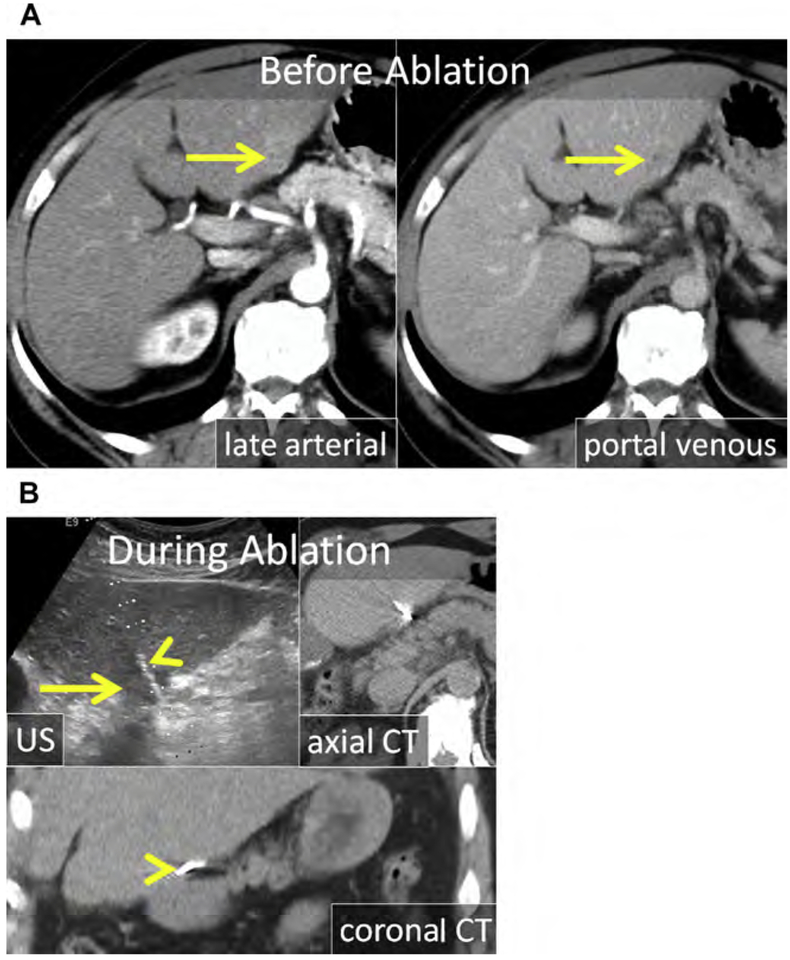
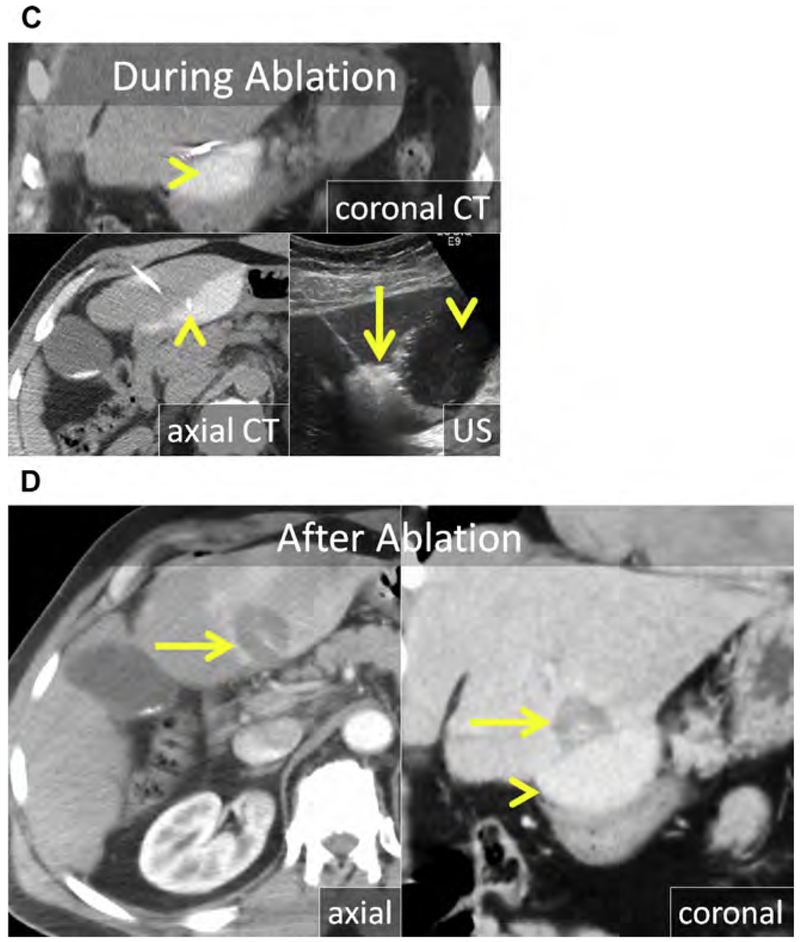
Fig. 8.
(A) Enhanced CT in the late arterial and portal venous phase shows an exophytic HCC projecting from the inferior left liver (arrows). (B) At US, the HCC is hypoechoic (arrow). The MW antenna is well seen at both US and CT (arrowhead). (C) Artificial ascites was used to displace the stomach and pancreas; a trocar needle was placed through the left liver and a 2% iohexol-enhanced saline solution was infused (arrowheads). At CT, the stomach wall and pancreas were adequately displaced. The gas cloud at US (arrow) encompasses the HCC including a margin. (D) Enhanced CT in the late arterial (axial) and portal venous phase (coronal reformat) immediately after MW ablation. The ablation encompasses the index lesion including a 5 mm margin (arrow) without damage to the stomach or pancreas. The stomach and pancreas remained safely displaced (arrowhead) throughout the procedure and were not injured (arrowhead).