Fig. 2.
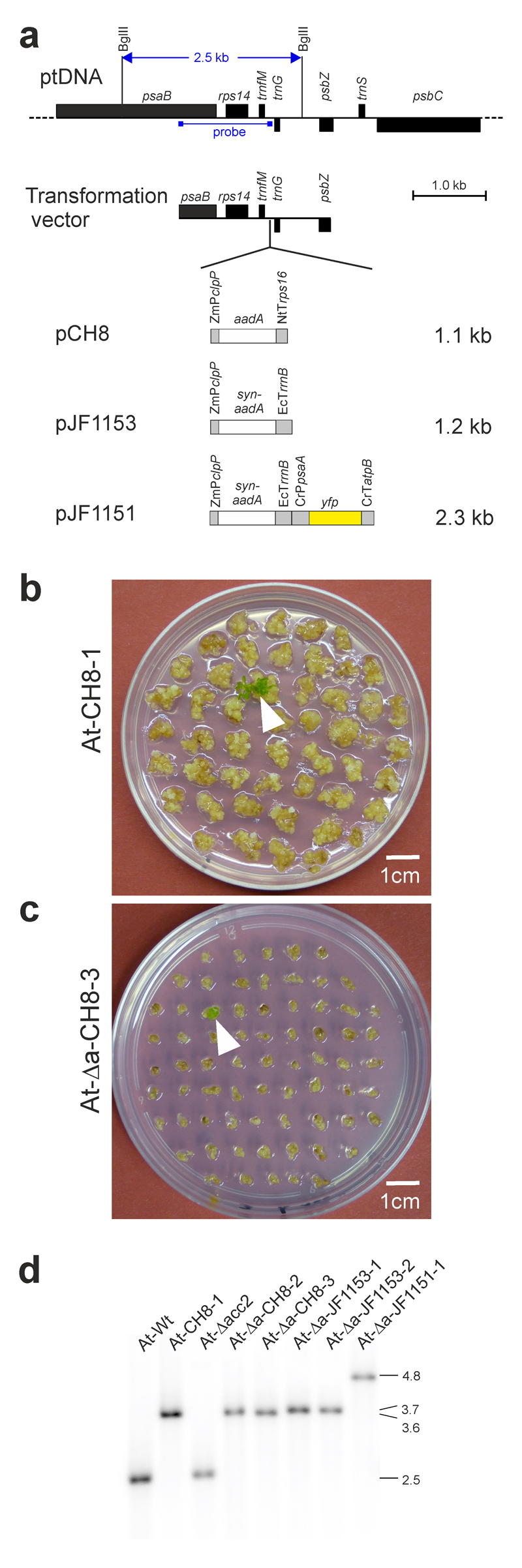
Construction of plastid transformation vectors and selection of transplastomic Arabidopsis plants. (a) Physical map of the targeting region in the plastid genome (ptDNA) of Arabidopsis and plastid transformation vectors. Genes above the line are transcribed from left to right, genes below the line are transcribed from the opposite strand of the ptDNA. The transgenes are inserted into the intergenic spacer between the trnfM and trnG genes within a cloned ptDNA fragment18 (Transformation vector). The location of two BglII restriction sites that were used for Southern blot analysis and the binding site of the hybridization probe is also indicated. The sizes of the transgene cassettes in the three vectors are given in kb. ZmPclpP: promoter of the plastid clpP gene from Zea mays (with the clpP 5’ UTR and the G10-derived Shine-Dalgarno sequence form phage T7; ref. 39); aadA: aadA gene from E. coli; syn-aadA: synthetic codon-optimized aadA gene; NtTrps16: 3’ UTR from the tobacco plastid rps16 gene; EcTrrnB: rRNA operon terminator from E. coli; CrPpsaA: promoter of the plastid psaA gene from Chlamydomonas reinhardtii; CrTatpB: 3’ UTR of the plastid atpB gene from C. reinhardtii. (b) Selection of a transplastomic line (white arrowhead) following bombardment of wild-type tissue with vector pCH8. These transformation experiments were repeated independently 507 times (cf. Table 1), and resulted in similar background growth of the bombarded calli. (c) Selection of a transplastomic line (white arrowhead) after bombardment of acc2 knock-out tissue (At-Δacc2) with vector pCH8. Note the much more efficient suppression of background callus growth from the acc2 knock-out tissue. For additional images, see Supplementary Figs. 4 and 6. The transformation experiments with the At-Δacc2 recipient line and vector pCH8 were repeated independently 98 times with similar results. (d) Southern blot analysis of transplastomic Arabidopsis lines. Total DNA extracted from regenerated plants growing under aseptic conditions was digested with BglII, separated by agarose gel electrophoresis and hybridized to a radiolabelled probe (cf. panel a). The sizes of hybridizing fragments are indicated in kb at the right. These experiments were repeated independently three times with similar results.
