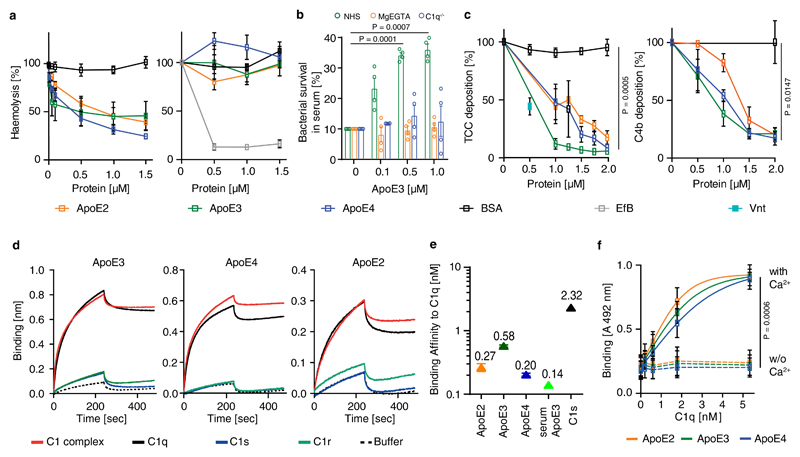
Figure 3. ApoE inhibits CCC initiation by high-affinity binding to C1q.
(a) ApoE inhibits CCC activation but not the alternative pathway. ApoE isoforms ApoE2, ApoE3, or ApoE4 were incubated in normal human serum (NHS), which was activated either via CCC buffer (left) (1% in GVB++) or alternative pathway buffer (right) (20% in MgEGTA); and lysis of sheep or rabbit erythrocytes by TCC was followed by measuring released haemoglobin at 415 nm. (b) ApoE was incubated with NHS in GVB++ buffer or Mg-EGTA buffer or with C1q-deficient serum in GVB++ to activate different complement pathways. Survival of E. coli was analyzed counting colony forming units. Survival of E. coli in normal serum was set as 10%. (c) ApoE isoforms inhibit the CCC at the level of TCC and C4b. ApoE isoforms in NHS were added to IgM-coated microtiter plates and TCC or C4b deposition was determined by specific antibodies, respectively. (d) Binding of C1, C1q, C1s, and C1r to ApoE isoforms was determined by biolayer interferometry as described in Methods. (e) The binding affinities of ApoE isoforms and C1s to C1q were determined by biolayer interferometry. ApoE proteins and C1s were biotinylated, immobilized on streptavidin-coated sensors, and C1q binding was determined by measuring changes of optical thickness on the sensor. (f) The ApoE-C1q interaction is dependent on Ca2+. Data represent means ± SEM of three independent experiments. Two-tailed Student´s t-test. BSA, bovine serum albumin; TCC, terminal complement complex; EfB, microbial inhibitor of the alternative pathway. Vnt: vitronectin. GVB: gelatin veronal buffer.