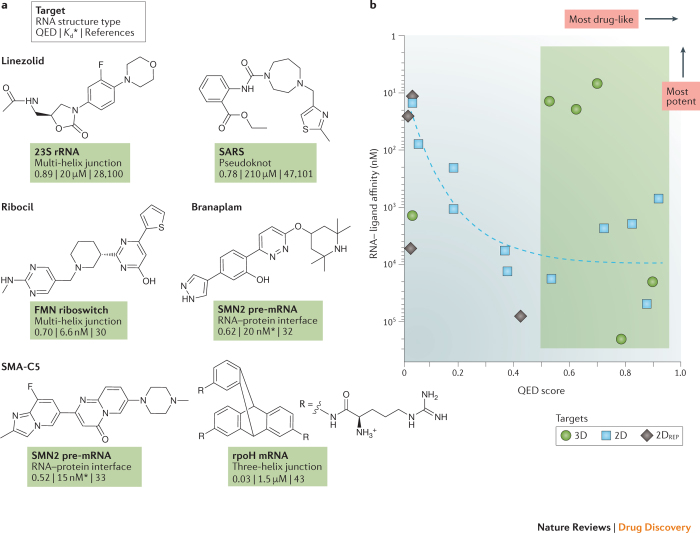
Figure 2. Instructional examples of bioactive small molecules that bind to RNA.
a | Molecules that bind RNA tertiary structures. Molecules are listed by their quantitative estimate of drug-likeness (QED) score (Box 1), with the most drug-like molecules towards the top and towards the left if the molecules are on the same row. The equilibrium dissociation constant (Kd) is listed for most molecules; if no Kd was available, the median inhibitory concentration (IC50) is provided instead (indicated by an asterisk). Molecular properties were calculated with SilicosIT. b | Relationship between QED scores and RNA binding affinity. Molecules targeting tertiary structures (shown in this figure; 3D targets) and those targeting secondary and repeat structures (from Fig. 3; 2D and 2DREP targets) are shown as circles, squares and diamonds, respectively. The green box highlights the region where most (five out of six) molecules that target RNA tertiary structures fall. The dashed blue curve highlights a trend for molecules targeting RNA secondary structures and repeat sequences: molecules with greater potency tend to have lower drug-likeness. FMN, flavin mononucleotide; rRNA, ribosomal RNA; SMN2, survival motor neuron protein.